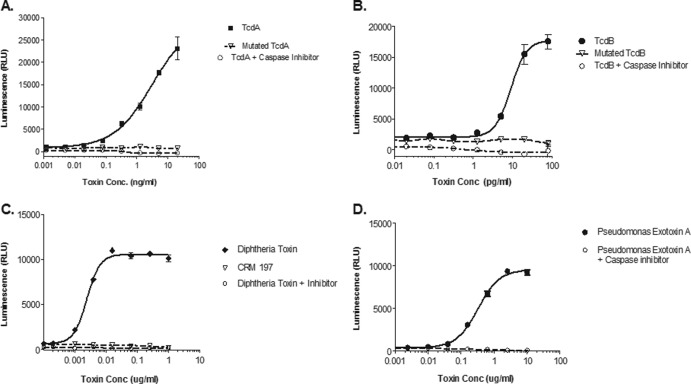
Fig 3.
Specificity of toxin-induced caspase activity in vitro was demonstrated by addition of 20 μM caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk (○) or genetic inactivation of toxin (△) compared to active toxins (closed symbols) for C. difficile TcdA (A), C. difficile TcdB (B), C. diphtheriae toxin (C), and P. aeruginosa exotoxin A (D). Genetically inactivated C. difficile toxins were produced from point mutations in the enzymatic domains of TcdA and TcdB. The inactive C. diphtheriae toxin CRM197 was produced by a single missense mutation (Gly52 to Glu52) within the fragment A region. Caspase induction was measured in toxin-treated cell cultures using Caspase-Glo 3/7 assay kit (Promega), and the results are shown as the mean luminescence (in relative light units [RLU]) ± the standard deviation for 3 replicate wells.