Figure 1.
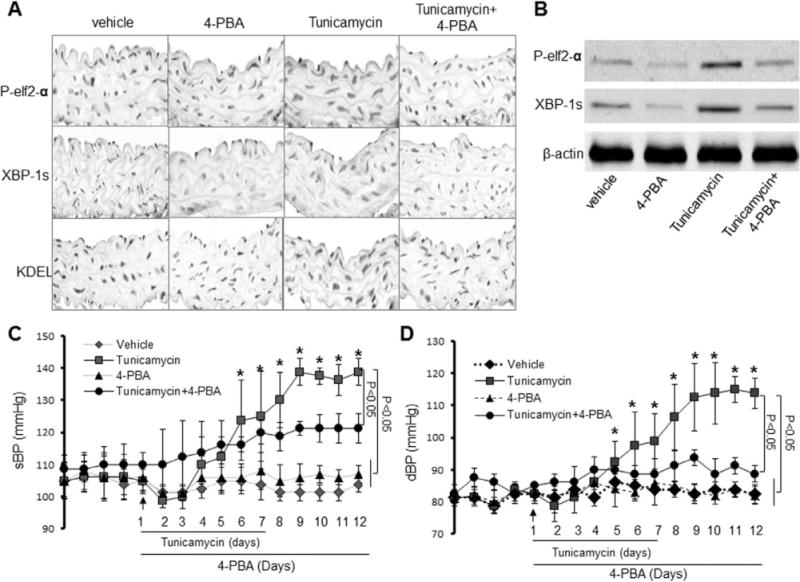
Acute infusion of Tunicamycin causes a 4-Phenyl butyric acid (4-PBA)-inhibitable high blood pressure in vivo. Mice were infused with Tunicamycin with or without 4-PBA. Blood pressures and heart rates were monitored by telemetry, as described in Materials and Methods. A, Effects of 4-PBA on Tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in aortas in vivo. The image is a representative of 5 images from ≥5 mice. B, 4-PBA reduces ER stress markers in Tunicamycin-induced ER stress in aortas in vivo. The blot is a representative of 6 blots from 6 individual experiments. C, Effects of 4-PBA on Tunicamycin-induced elevation of systolic blood pressure (sBP); n=12 to 16 in each group. *P<0.05. D, Effects of 4-PBA on Tunicamycin-induced changes of diastolic blood pressure (dBP). n=12 to 16 in each group, *P<0.05. The data from C and D were analyzed using the 2-way ANOVA for repeated measures followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test.
