Figure 6.
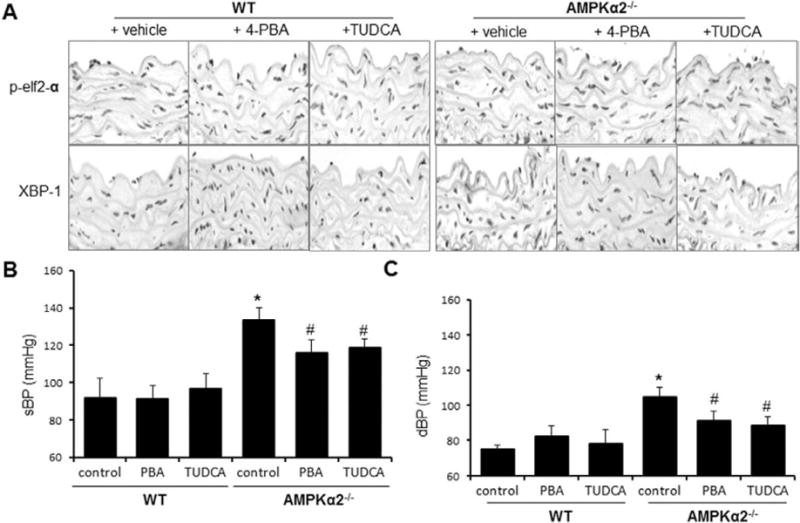
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress chaperones normalize blood pressure in AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) α2−/− mice. Wild-type (WT) mice and AMPKα2−/− mice were orally administered with 4-phenyl butyric acid (4-PBA; 1 g/kg per day) or tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA; 0.5 g/kg per day) for 3 weeks, as described in Materials and Methods. A, 4-PBA and TUDCA suppress aberrant ER stress in AMPKα2−/− mice in vivo. ER stress markers were detected in immunohistochemical staining with the specific antibodies. The image is a representative of 6 images from 6 mice. B, Effects of 4-PBA and TUDCA on systolic blood pressure (sBP); n=12 in each group. *P<0.05 WT vs AMPKα2−/−. #P<0.05 vs AMPKα2−/− vs AMPKα2−/− mice treated with 4-PBA or TUDCA. C, Effects of 4-PBA and TUDCA on diastolic blood pressure (dBP); n=12 in each group. *P<0.05 WT vs AMPKα2−/−. #P<0.05 vs AMPKα2−/− vs AMPKα2–/– mice treated with 4-PBA or TUDCA. Statistical analysis for B and C was performed by using a 2-tailed Student t test between 2 groups.
