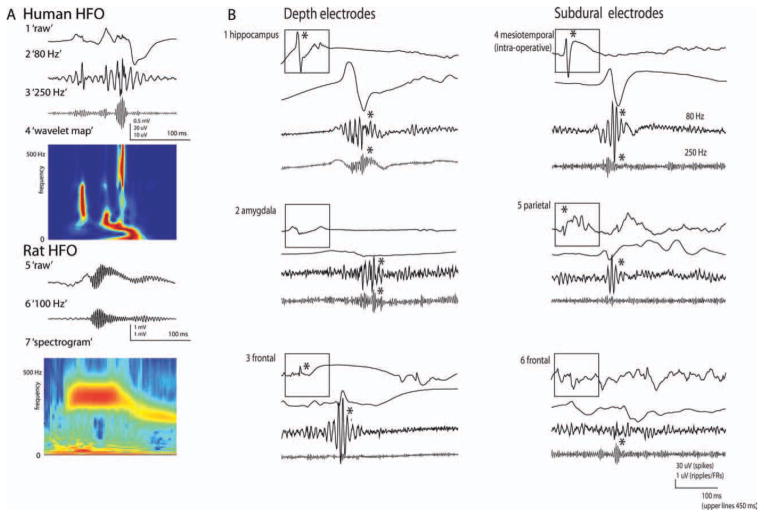
FIGURE 1.
Examples of HFOs. (A) HFOs recorded with depth macroelectrode in human (1–4) and rat (5–7) hippocampal area. (1) Raw intracranial EEG with sharp wave from human hippocampal area (macroelectrode). (2 and 3) Filtered with high-pass filter of 80Hz and 250Hz. Note the differences in amplitude scales. Such an event would not stand out in normal EEG. (4) Wavelet transform of frequencies up to 500Hz. (5) Raw intracranial EEG data from rat with right intrahippocampal injection of tetanus toxin (microelectrode). A fast ripple with peak frequency 359Hz followed by activity at 240Hz is visible in the raw data. (6) Filtered with high-pass filter of 100Hz. (7) Spectrogram up to 500Hz after Fourier transformation. (B) HFOs recorded with depth and subdural macroelectrodes, in mesiotemporal areas and neocortical areas in patients with epilepsy. For each event the display shows the standard EEG signal, the same signal with extended time scale and this signal after 80Hz and 250Hz high-pass filtering. Different examples are shown from different sites. This illustrates that all combinations are possible: spike with ripple and fast ripple (1+4), ripple and fast ripple without spike (2), spike with ripple without fast ripple (3+5) and fast ripple without ripple or spike (6). An asterisk (*) means that the event was marked at this frequency. EEG = electroencephalogram; FRs = fast ripples; HFO = high-frequency oscillation.