Figure 3. HbpS binds Fe(II) and oxidizes it to Fe(III).
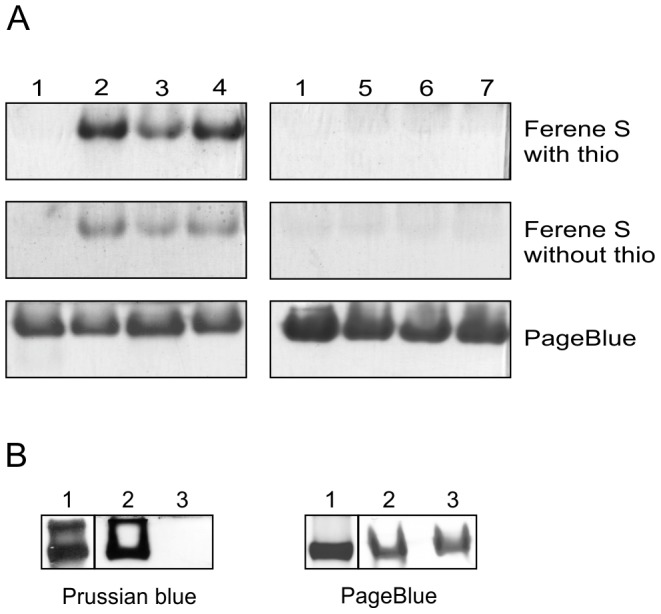
(A) Aliquots of wild-type HbpS without previous incubation with iron ions (lane 1) and incubated with either the ferrous iron salts Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2 (lane 2), FeCl2 (lane 3) and FeSO4 (lane 4) or with the ferric iron salts FeNH4(SO4)2 (lane 5), FeCl3 (lane 6) and Fe(ClO4)3 (lane 7) were loaded onto native PAA gels (3x). Ferene S staining was performed with (top) or without thioglycolic acid (thio) (middle). As a control proteins were stained with PageBlue (bottom). (B) Wild-type HbpS (lane 2) and the mutant HbpS protein E78A/E81A (lane 3) were incubated with Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2. Reaction mixtures were split into two parts and proteins were subjected to native PAGE. PageBlue was used to stain proteins (right) and Prussian blue staining to specifically detect Fe(III). Equine spleen type ferritin (lane 1) was used as a positive control for Prussian blue staining.
