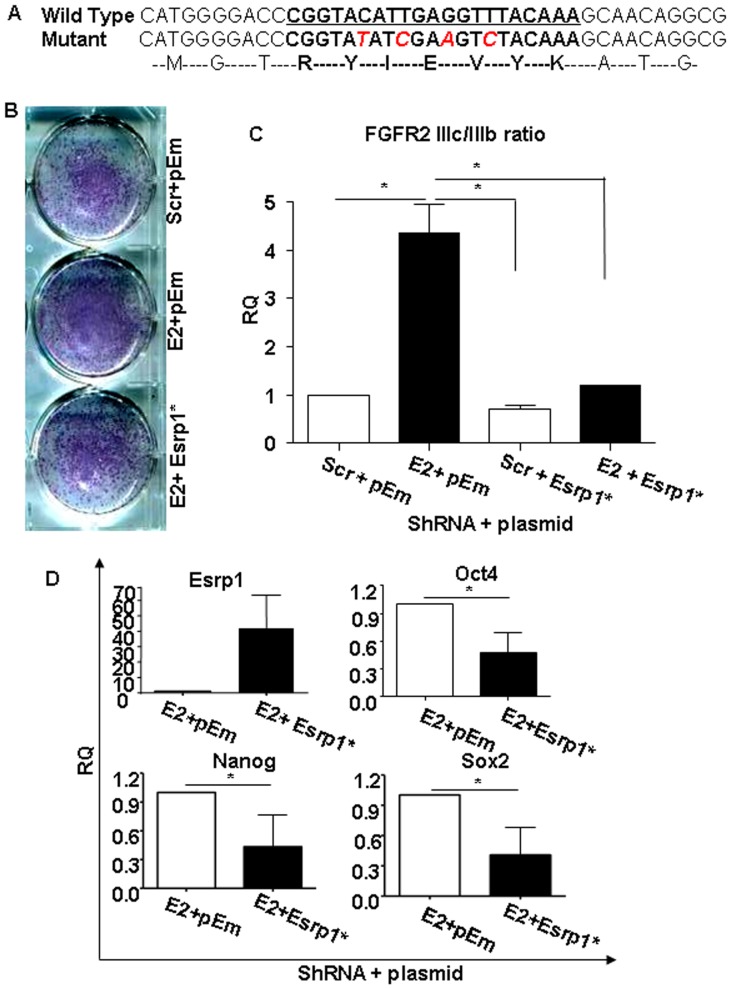
Figure 3. Rescue of Esrp1-depleted cells and differentiation potential of Esrp1-depleted ES cells.
A. Sequence of Esrp1 cDNA showing ShRNA binding site (in bold and underlined) and the position of inserted mutations (red). The corresponding amino acid sequence is shown as well. B. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining of Scr and Esrp1-depleted ES cells transiently transduced either with empty vector (pEm) and with the ShRNA-immune Esrp1-GFP cDNA (Esrp1*) (n = 3). C. qRT-PCR analysis of FGFR2 IIIc/IIIb ratio in Scr and Esrp1-depleted ES cells transiently transduced either with empty vector (pEm) and with the ShRNA-immune Esrp1-GFP cDNA (Esrp1*) showing a reduction in this ratio upon rescue. RQ is relative quantity (n = 3). D. qRT-PCR analysis of Esrp1, Oct4, Nanog and Sox2 mRNA in Esrp1-depleted ES cells transfected with pEm or Esrp1* expression vectors showing reduction in the expression of these genes upon rescue. RQ is relative quantity (n = 3).