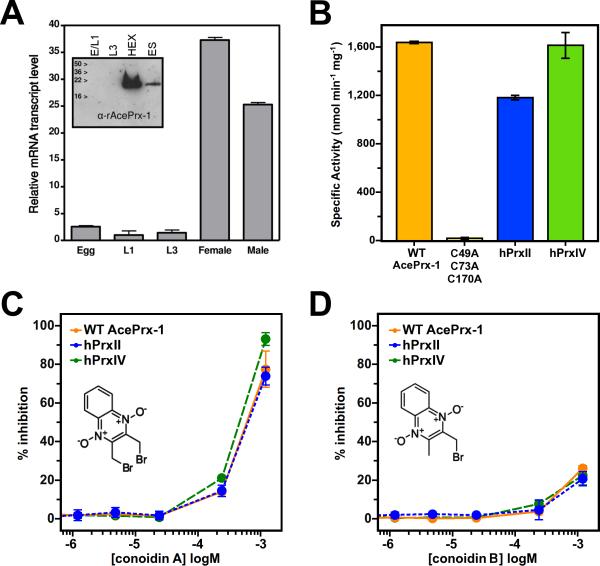
Figure 2. AcePrx-1 is expressed in adult hookworms and is inhibited by conoidin A.
A. Analysis of AcePrx-1 mRNA levels and protein expression throughout the life cycle of A. ceylanicum shows that AcePrx-1 is highly expressed in adult hookworms compared to egg (E), early larval stage (L1) or infectious larvae (L3).
B. Specific activity of AcePrx-1 as determined by monitoring the consumption of H2O2 in an iron-based colorimetric assay. Activity of human peroxiredoxins-II and -IV are provided for comparison, with the C49A/C73A/C170A AcePrx-1 mutant used as a negative control.
C-D. Inhibition of AcePrx-1, hPrxII, and hPrxIV activity by conoidin A (C) and conoidin B (D). The lack of inhibitory activity of conoidin B in the concentration range assayed may be due in part to the low solubility of conoidin B.