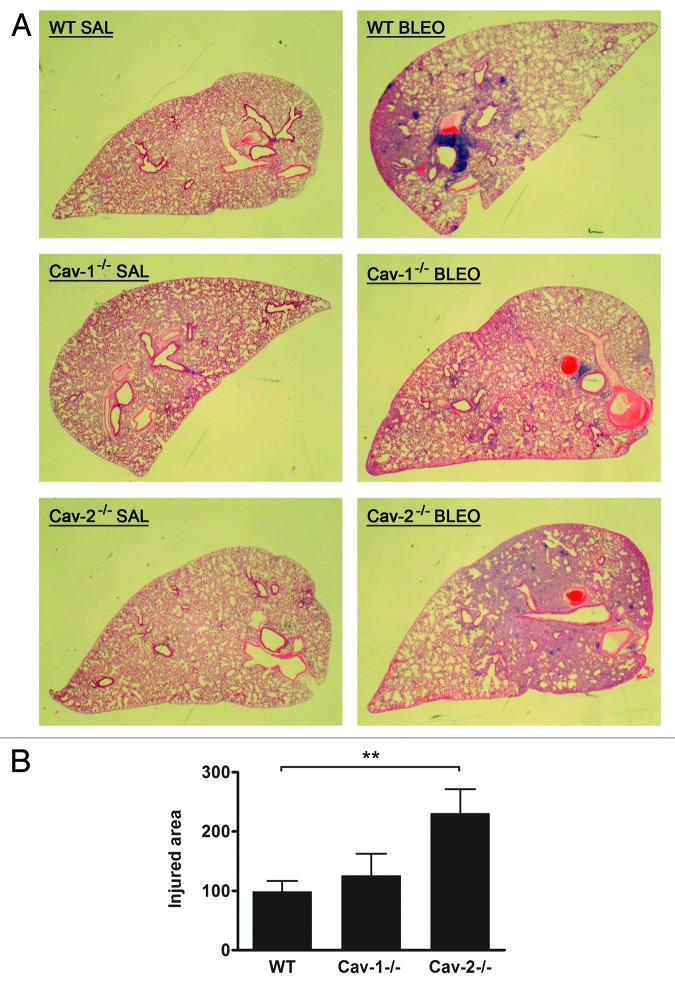
Figure 2.Cav-2−/− mice are more susceptible to bleomycin-induced lung injury. (A) Cav-2−/− mice show larger areas of injured parenchyma after bleomycin instillation. Wild-type, Cav-1−/−, and Cav-2−/− mice were intratracheally instilled with saline or bleomycin (1 U/kg) (n-12–22 for each group). Fourteen days later, the left lung was processed for histological analysis and stained with H&E. Bleomycin leads to reorganization of the lung parenchyma characterized by thickened alveolar septa and accumulation of proliferating and inflammatory cells. (B) Quantification of lung injury after bleomycin instillation. Lung injury was quantified by measuring the percentage of total area of the section composed of reorganized parenchyma. Measurement of the total and damaged areas was achieved with the ImageJ software. Data were expressed as a percentage of the WT group (**P < 0.01, n = 12–22 for each group).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.