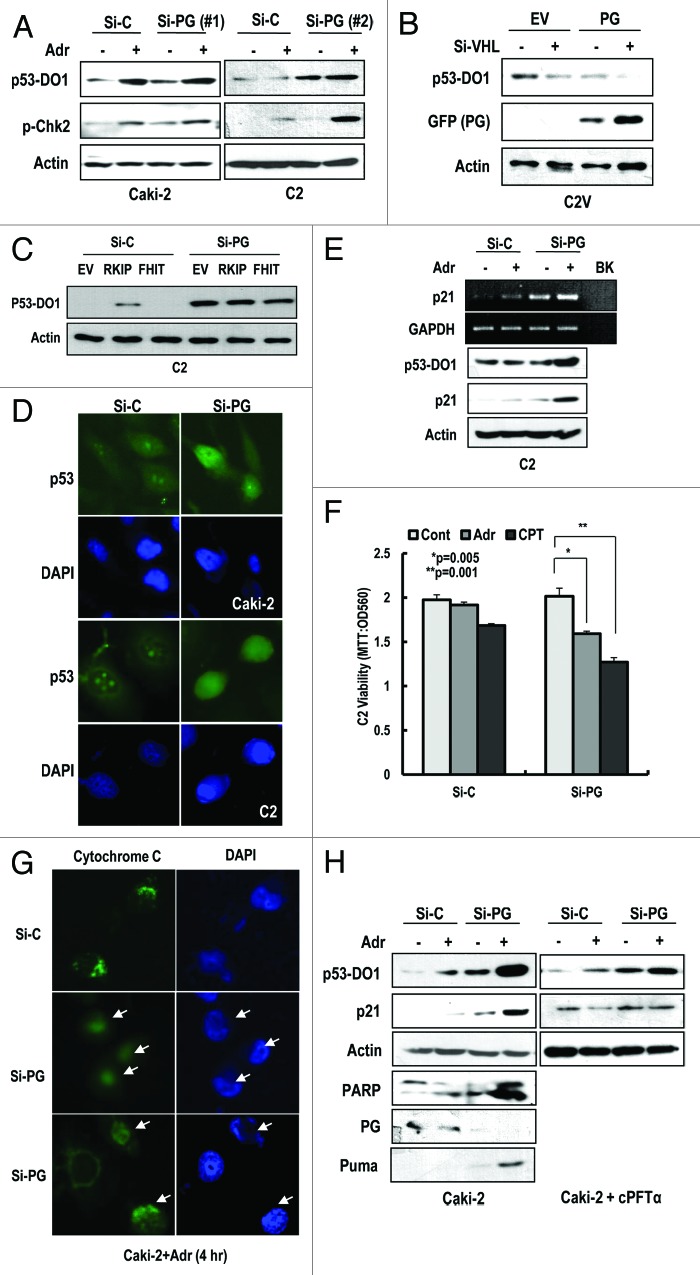
Figure 3. Progerin suppresses p53. (A) Si-progerin (Si-PG) induces p53 expression in Caki-2 and C2 cell line. These cells were transfected with si-C or si-PG for 24 h. After washing, cells were incubated with 1 μg/ml of adriamycin (Adr) for 2 h. (B) Progerin suppresses p53 expression in VHL-expressed C2V. C2V cells were transfected with progerin (PG) with/without si-VHL for 24 h. VHL knockdown could enhance the PG-induced p53 suppression. (C) FHIT or RKIP do not induce p53 in C2 cells. Because FHIT is located in the same chromosome as pVHL and frequently deleted in RCCs, we examined the effects of RKIP and FHIT on p53. However, these genes did not significantly induce p53 compared with si-PG. (D) IF staining of p53 in si-progerin (Si-PG)-transfected Caki-2 and C2 cells. Increased and nuclear localized p53 could be detected by IF with p53 (DO-1) antibody. (E) Si-progerin (Si-PG) induced p21 at the transcription and translation level. To address the functionality of p53, we measured the expression of p21 using RT-PCR and WB analysis. (F) Si-progerin (Si-PG) enhances the sensitivity to DNA damaging agents in C2. Cells were transfected with the indicated si-RNA for 24 h and incubated with adriamycin (Adr;1 μg/ml) or camptothecin (CPT: 1 μM) for 6 h. After washing, cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Data were analyzed with student’s t-test. (G) Si-progerin (Si-PG) can promote apoptosis. Caki-2 cells were transfected with si-PG or si-C for 24 h and incubated with adriamycin (Adr 2 μg/ml) for 6 h. Cells were fixed and stained with cytochrome C antibody. Compared with si-C, in which cytochrome C was stained as a cytoplasmic punctured pattern, diffused cytochrome C was detected in si-PG-transfected cells (arrows). (H) Si-progerin (Si-PG) can induce PUMA and PARP cleavage. To confirm that si-PG could induce apoptosis, we examined the expression of PUMA and PARP cleavage. cPTFα blocked the induction of p21 by si-PG or Adr, indicated that the effect of si-PG was dependent on p53 transcription activity.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.