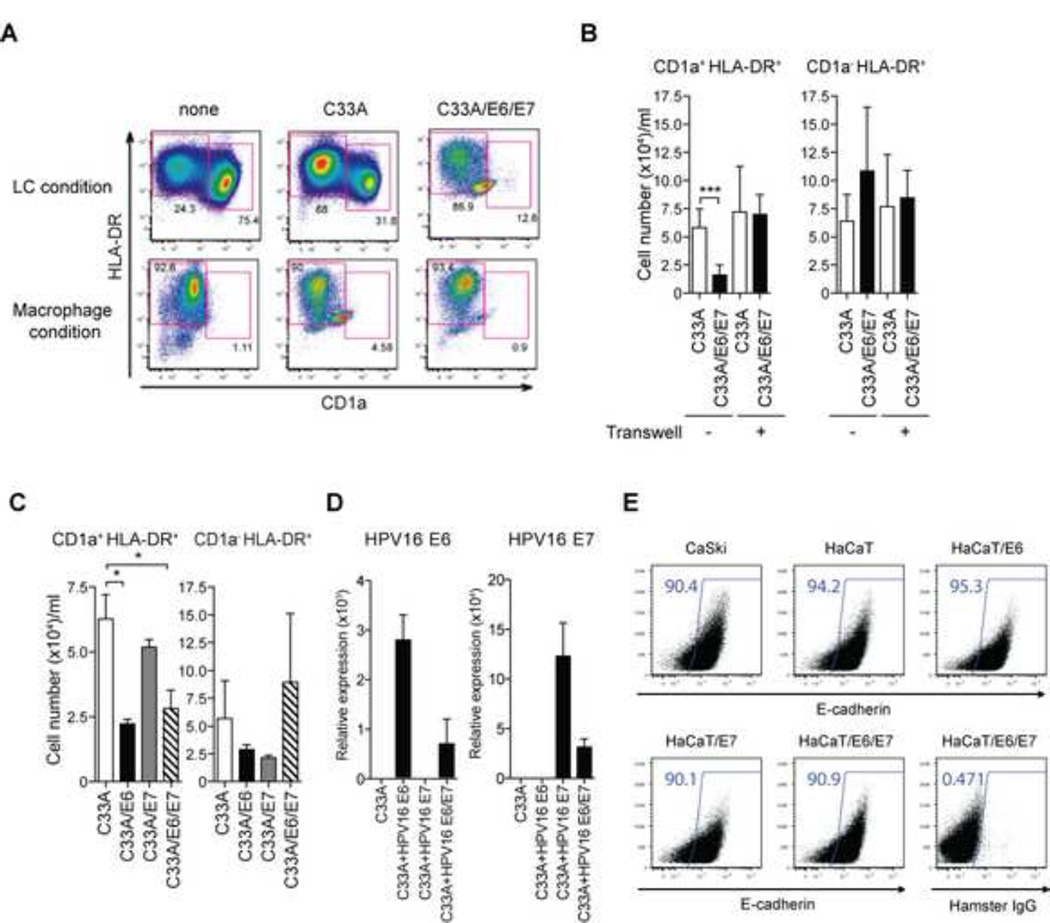
Figure 3. High-risk HPV16 E6 but not E7 impairs the differentiation of LCs from blood CD14+ monocytes in a contact-dependent manner.
CD14+ monocytes were co-incubated with UV-treated HPV− C33A cells containing the empty vector (C33A) or HPV16 E6 and E7-transduced C33A cells in the presence of GM-CSF/IL-4/TGF-β (LC condition) or GM-CSF (Macrophage condition) for 7 days. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for the expression of CD1a and HLA-DR. (B) CD14+ monocytes were co-incubated with UV-treated transduced C33A cells either together or separately in Transwell. The average numbers of differentiated CD1a+ HLA-DR+ LCs obtained from at least three donors are depicted. (C) CD14+ monocytes were co-incubated with UV-treated vector-transduced or HPV16 E6 and/or E7-transduced C33A cells in the presence of GM-CSF/IL-4/TGF-β for 7 days. The average numbers of LCs cultured in the presence of C33A transduced with the indicated viral genes obtained from at least three donors are depicted. (D) Expression levels of HPV16 E6 and/or E7 in C33A transduced with the indicated viral genes were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. (E) C33A, Caski, HaCaT or HaCaT expression HPV16 E6 and/or E7 were stained with antibody to E-cadherin or isotype control. Error bars indicate SEM. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.