Figure 4.
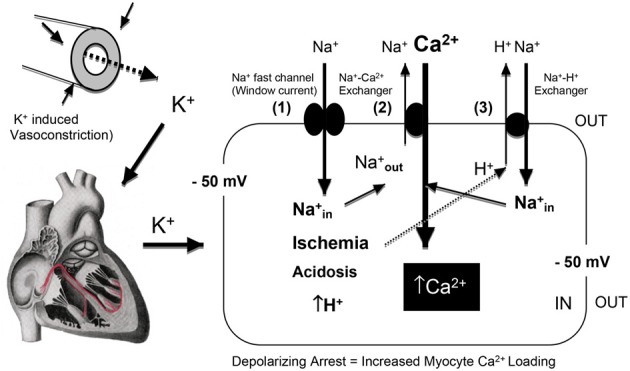
A schematic of the effect of hyperkalemia and prolonged myocardial membrane depolarization on Na+ entry through the “window current” and the net influx of Ca2+ into the myocardial cell via the reversal of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger [3Na+ ions are extruded in exchange for 1 Ca2+ entry (Bers and Despa, 2009) at a membrane potential of −50 mV (Baczko et al., 2003)]. Global or regional ischemia and metabolic acidosis impact further on Ca2+ loading, with increases in intracellular H+ further activating the Na+/H+ exchanger (Avkiran, 2001) resulting in 1Na+ ion being exchange for 1 H+ ion. The diagram was adapted from Bers and colleagues (Bers et al., 2003; Bers and Despa, 2006).
