Table 1. Statistics of real networks and their random counterparts. N is the number of nodes, E is the number of edges, C is the average clustering coefficient averaged only over nodes with degrees k ≥ 2. We also show the number of disconnected components (clusters) and the relative size of the giant component. Error bars are computed as the standard deviation of the corresponding metric as obtained from a sample of 10 network realizations. Figures without errors did not show any significant difference between different samples.
| N | E | C | # of clusters | Giant component | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internet | 23752 | 58416 | 0.61 | 3 | 99.98% |
| Internet clique-based model | 23800 ± 200 | 50000 ± 10000 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 2200 ± 400 | (75 ± 4)% |
Internet random 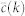
|
23752 | 58416 | 0.61 | 16 ± 4 | (99.84 ± 0.06)% |
Internet random 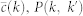
|
23752 | 58416 | 0.61 | 4 ± 1 | (99.96 ± 0.02)% |
| PGP | 57243 | 61837 | 0.50 | 16221 | 18.65% |
| PGP clique-based model | 62000 ± 1000 | 57200 ± 200 | 0.506 ± 0.005 | 13700 ± 200 | (37 ± 1)% |
PGP random 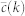
|
57243 | 61837 | 0.487 ± 0.001 | 15550 ± 60 | (21.3 ± 0.4)% |
PGP random 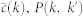
|
57243 | 61837 | 0.493 ± 0.001 | 15810 ± 20 | (22.3 ± 0.3)% |
| E. Coli | 1010 | 3286 | 0.48 | 2 | 99.8% |
| E. Coli clique-based model | 1010 ± 40 | 3300 ± 700 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 7 ± 3 | (97.9 ± 0.6)% |
E. Coli random 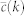
|
1010 | 3286 | 0.48 | 2.2 ± 0.9 | (99.7 ± 0.3)% |
E. Coli random 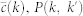
|
1010 | 3286 | 0.48 | 7 ± 2 | (98.2 ± 0.6)% |
