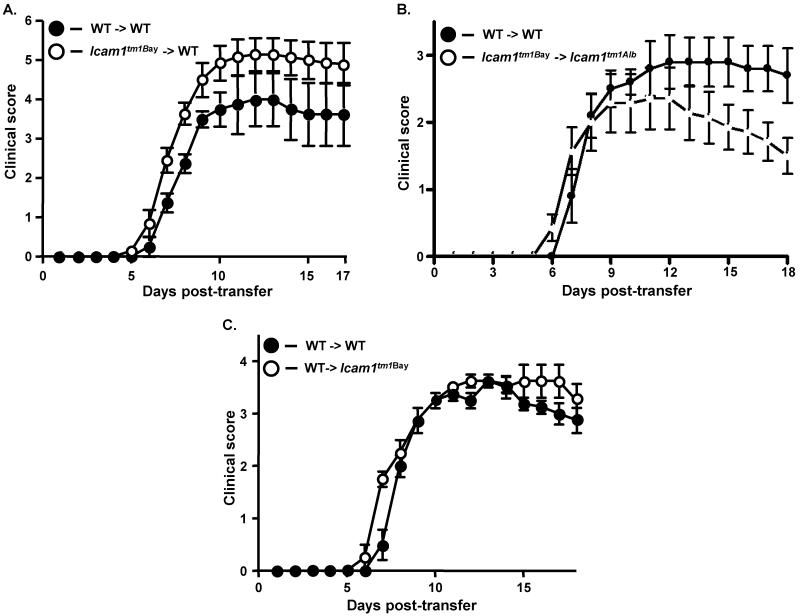
Fig. 4.
Encephalitogenic T cells from Icam1tm1Bay mice drive the development of EAE in wild type and Icam1tm1alb mice. A, Transferred EAE was induced in wild-type (n=7) mice by injecting encephalitogenic T cells (~5 × 106) derived from Icam1tm1Bay mice with active EAE. As a control transferred EAE was induced in wild type mice (n=4) by injecting encephalitogenic T cells (~5 × 106) derived from wild-type mice with active EAE. Results shown are the daily mean clinical score from three separate experiments. B, Transferred EAE was induced in Icam1tm1alb (n=7) mice by injecting encephalitogenic T cells (~5 × 106) derived from Icam1tm1Bay mice with active EAE. Control transferred EAE in wild type mice (n=5) was run in parallel. Results shown are the daily mean clinical score from two separate experiments. C, Transferred EAE was induced in wild type (n=4) and Icam1tm1Bay mice (n=4) mice by injecting encephalitogenic T cells (~5 × 106) derived from wild-type mice with active EAE. Results shown are the daily mean clinical score from two separate experiments.