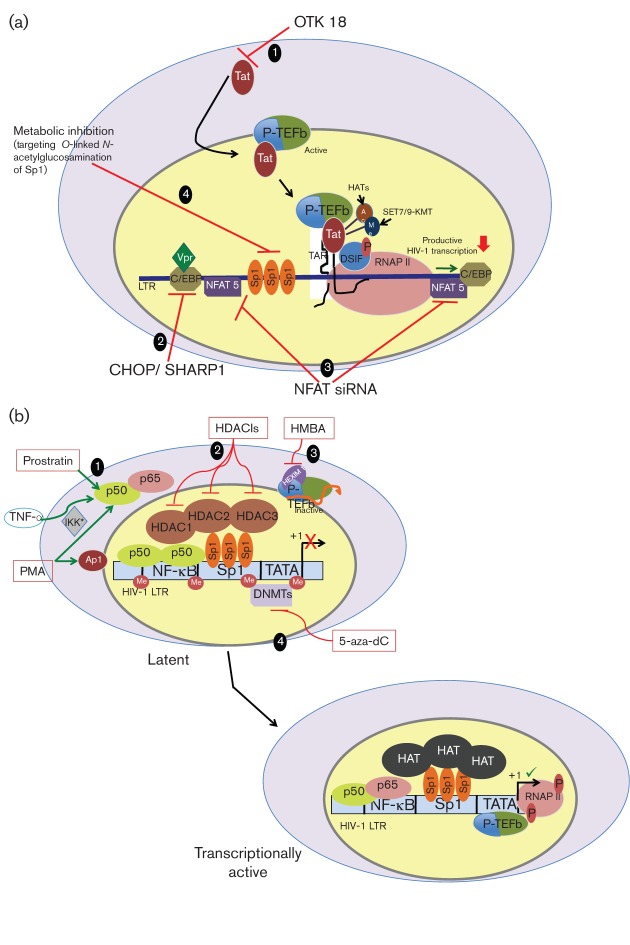
Fig. 4.
Therapeutic strategies for HIV-1. (a) Strategies to suppress HIV-1 transcription: (1) inhibit Tat-mediated transactivation using the C2H2 zinc finger protein OTK18, resulting in overall inhibition of transcription from the LTR. (2) Target the C/EBP protein, a crucial transcriptional regulator in cells of the monocyte–macrophage lineage, by using overexpression of cellular inhibitors like CHOP/SHARP1 to suppress LTR-directed transcription. (3) Evaluate inhibition of the NFAT family of proteins C as a potential therapy to block HIV-1 expression. (4) Regulate the function of the Sp1 transcription factor through post-translational modifications including O-linked N-acetylglucosamination; evaluate strategies to inhibit the relevant enzymes to maintain HIV-1 in an inactive state. (b) Strategies to purge HIV-1: (1) activate NF-κB to achieve a stimulated expression from the latent integrated HIV-1 genome. The homodimeric p50 form of NF-κB recruits HDACs during latency. In resting CD4+ T-cells, the activating p50–p65 heterodimer of NF-κB is sequestered in the cytosol; use of activators like phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, TNF-α and prostratin, which activate IκB kinase and induce nuclear translocation of p50–p65 and recruitment of HATs to the NF-κB sites, can result in activation of HIV-1 transcription. (2) Use class I selective HDAC inhibitors that inactivate HDACs 1, 2 and 3 at the LTR and result in unrestricted action of HATs that are recruited to the LTR by various transcription factors, resulting in acetylation of histones at nucleosomes near the site of initiation of LTR-directed transcription. (3) Use HMBA to release P-TEFb from inactive complexes with HEXIM 1, resulting in phosphorylation of RNAP II CTD and subsequent shift to processive transcription of the integrated HIV-1. (4) Reverse transcriptional silencing imposed by the methylation of cytosine residues at the LTR by DNA methyltransferases by inhibiting the enzyme using 5-aza-2′ deoxycytidine, resulting in stimulation of HIV-1 transcription.