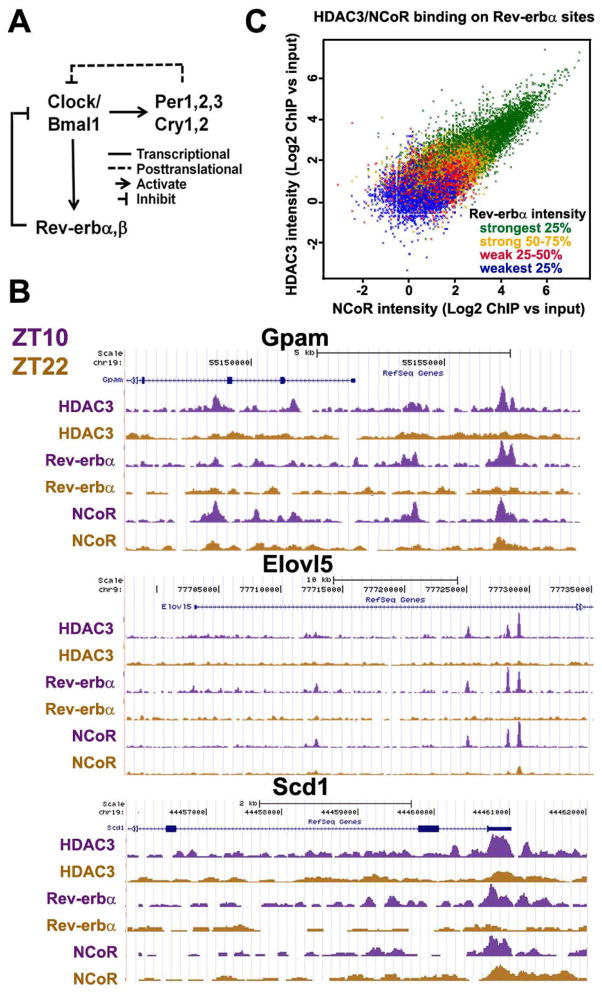
Figure 3.
Rev-erbα controls circadian recruitment of HDAC3 to the genome. (A) The core molecular circadian clock machinery. Clock/Bmal1 heterodimer transcriptionally activate Period (Per 1, 2, 3), Cryptochrome (Cry 1, 2), and Rev-erbα&β. Per and Cry interferes with the activity of Clock/Bmal1 proteins, while Rev-erb represses transcription of Clock/Bmal1 genes. (B) Circadian occupancy of HDAC3, NCoR, and Rev-erbα on hepatic lipogenic genes as viewed by the UCSC genome browser. Gpam, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1, mitochondrial; Elovl5, fatty acid elongase 5; Scd1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1. (C) For all sites occupied by Rev-erbα at ZT10 in mouse liver, ChIP-seq signal intensities for Rev-erbα, NCoR, and HDAC3 were normalized to reads per million (rpm) and computed as log2 of the ratio of ChIP rpm to input rpm. To analyze the 3-way correlation of binding affinities of the 3 factors, scatter plot with HDAC3 and NCoR signal intensities was color-coded by the quartile of signal intensity for Rev-erbα.