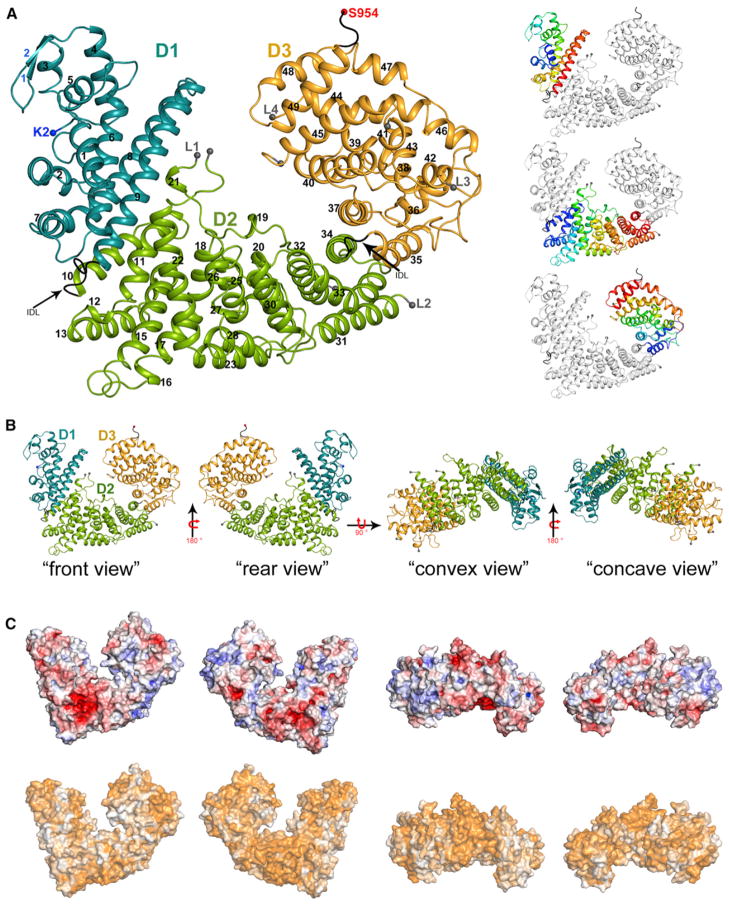
Figure 1. Structure and Surface Properties of ScNup192(2–960).
(A) Overall structure of ScNup192(2–960) is shown as a cartoon representation with the D1, D2, and D3 domains colored cyan, green, and gold, respectively. Interdomain loops comprising residues 204–211 and 663–670 are marked by arrows. Residues at the boundaries of the disordered loops are depicted as gray spheres, and the beginning of these loops are marked as L1, L2, L3, and L4. Side panels show individual D1, D2, and D3 domains as the blue to red rainbow from N to C terminus. Secondary structure elements are shown as defined by the DSSP (Kabsch and Sander, 1983) program. Strands of the β-hairpin are labeled in blue; additionally, helices are numbered consecutively with 310 helices treated as α helices for simplicity. See also Figure S1.
(B) Representations of the front, rear, convex, and concave views of the ScNup192(2–960) are illustrated with the D1, D2, and D3 domains colored cyan, green, and gold, respectively.
(C) The top row shows electrostatic potential of ScNup192(2–960) plotted onto its solvent accessible surface. Missing side chains and charges were assigned for ScNup192(2–960) structure using Protein Data Bank (PDB) 2PQR (Dolinsky et al., 2007), and electrostatic surface was calculated using APBS (Baker et al., 2001) within PyMOL. Negative (−7 kT/e) and positive (+7 kT/e) potentials are shown in red and blue, respectively. The bottom row shows conservation of 11 different fungal Nup192 sequences plotted onto the surface of ScNup192(2–960) structure with least to absolutely conserved residues colored as a gradient from white to orange. See also Figure S2.