Figure 6.
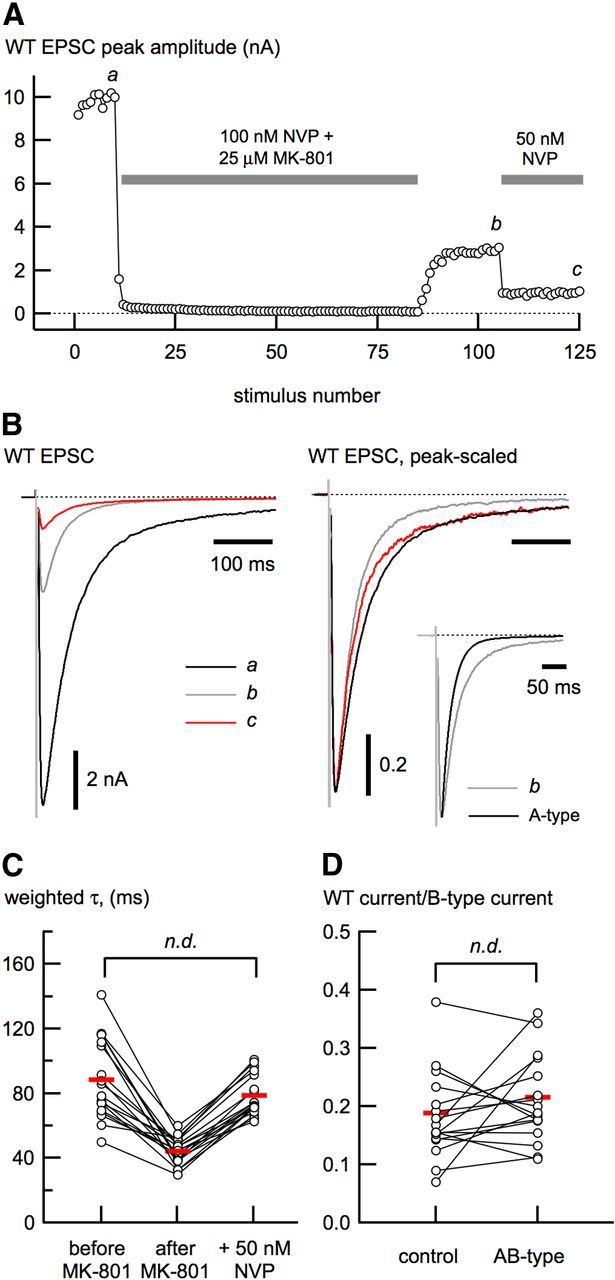
Functional isolation of synaptic triheteromeric (AB-type) receptors. A, Outline of our strategy for isolation of AB-type NMDA receptor-mediated EPSCs in wild-type (WT) neurons. EPSCs were evoked at low frequency (0.1 Hz) while cells were perfused with NVP and MK-801 to prevent A-type channels from opening and to progressively block the remaining channels (B-type and AB-type). The NVP/MK-801 solution was removed, leaving EPSCs that result from A- and AB-type receptors (b). To enrich the remaining EPSC with AB-type receptors, the neurons were perfused with 50 nm NVP to block the majority of A-type receptors. B, EPSCs shown from different times in the isolation protocol (a–c) shown in A, indicating their relative amplitudes (left) and peak-scaled (right) to show how the deactivation changes during the course of the experiment. The inset (right) shows the EPSC at b compared with the deactivation of A-type EPSCs alone. The τw (C) and the estimate of the maximal B-type receptor contribution (D) do not differ between control and enriched AB-type receptors.
