FIGURE 3.
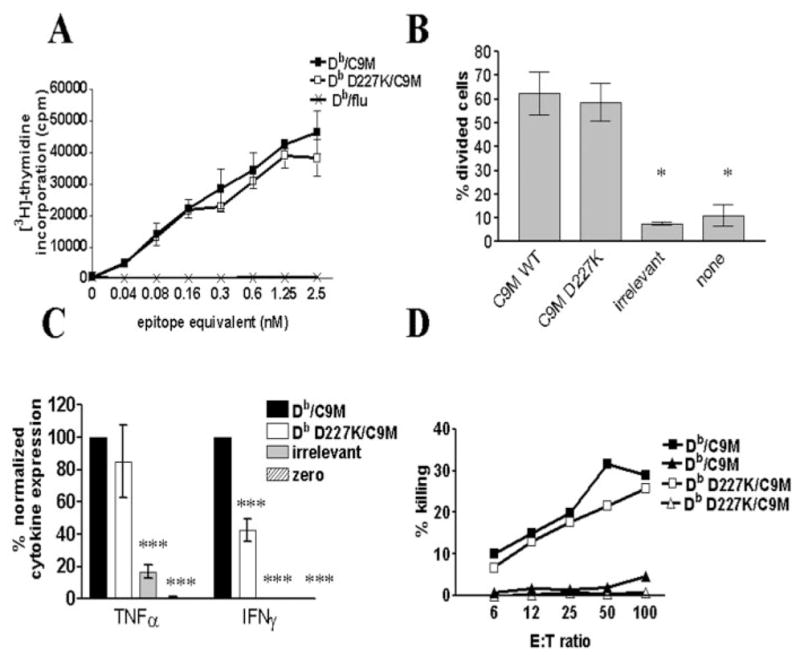
Higher affinity MHC-TCR interaction overcomes need for CD8 engagement. A, CD8+ P14 splenocytes were stimulated with Db/C9M (■), Db D227K/C9M (□), or control (×) tetramers, then measured for their ability to proliferate in vitro. Samples were assayed in triplicate, and the average was plotted with the error bars indicating ±SEM. Data are representative of five independent experiments. B, Measurement of in vivo proliferative ability of cells stimulated with Db/C9M or Db D227K/C9M. Db D227K/C9M-stimulated CD8+ T cells illustrate similar proliferative ability, as compared with cells stimulated with Db/C9M tetramers (*, p ≤ 0.05). In vivo proliferation was performed using four mice per group, the percentage of divided cells was calculated as in Fig. 2, and the data are representative of two independent experiments. C, IFN-γ production by Db D227K/C9M-stimulated cells is significantly lower as compared with Db/C9M stimulation (***, p ≤ 0.001). Each sample was assayed in triplicate and the amount of cytokines produced was normalized to cytokine levels produced by Db/gp33 stimulation. Data are representative of two independent experiments. D, CTL activity of tetramer-stimulated P14 cells. Target cells were pulsed with relevant (■,□) and irrelevant peptide (▲,△). Db D227K/C9M-stimulated cells are shown with open symbols, while Db/C9M-stimulated cells are shown with filled symbols. The average of three replicates per ratio is plotted, and data are representative of three independent experiments.
