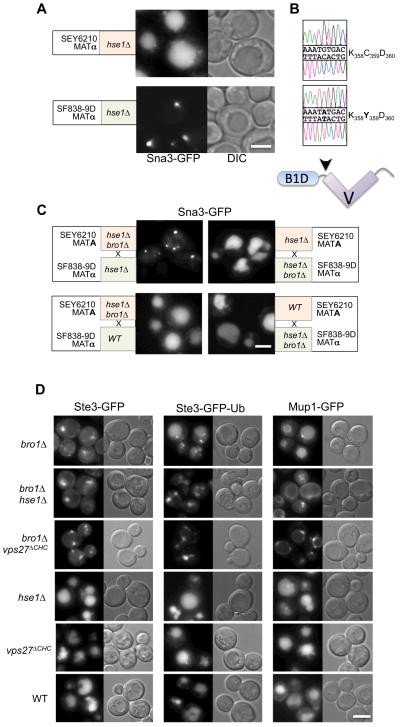
Figure 1. Synthetic interaction between Bro1 and ESCRT-0.
A. Localization of Ste3-GFP in hse1Δ null mutants generated from the SEY6210 and SF838-9D parental strains. Shown are DIC and GFP-fluorescence images
B. Chromatograms of BRO1 ORF sequence (Sanger sequencing of PCR-amplified DNA) from SEY6210 cells (top) or SF838-9D cells (bottom). Arrowhead in schematic below indicates location of residue 359 between the N-terminal Bro1 homology domain (B1D) and the middle V domain.
C. Demonstration that the bro1 Y359 allele causes a synthetic phenotype with hse1Δ. BRO1Δ was disrupted in MATA SEY6210 hse1Δ or MATα SF838 hse1Δ haploids, and these were subsequently mated to form diploids. Sorting of Sna3-GFP to the vacuole lumen was defective in hse1Δ homozygous diploids with only the bro1Y359 allele from the SF838-9D haplotype. However, Sna3-GFP was correctly sorted in hse1Δ homozygous diploids with only BRO1C359 from the SEY6210 haplotype. Diploids heterozygous for both hse1Δ bro1Δ also sorted Sna3-GFP properly regardless of from either haplotype.
D. Localization of Ste3-GFP, Ste3-GFP-Ub, and Mup1-GFP in SEY6210 cells of the indicated genotypes: wild-type (WT); bro1Δ null alone; bro1Δ hse1Δ double null; Vps27 lacking its C-terminal clathrin-binding motif (vps27ΔChc1); hse1Δ alone or the vps27ΔChc1 mutation alone. Bar=5μM