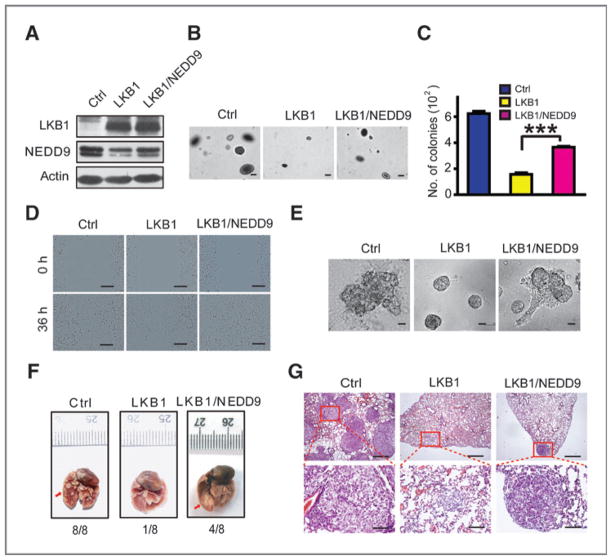
Figure 2.
Ectopic NEDD9 expression partially reverses the inhibitory function of LKB1 upon colony formation, migration, and invasion of human lung cancer cells. A, Western blot detection of LKB1 and NEDD9 expression in A549 cells with ectopic LKB1 and/or NEDD9 expression. B and C, colony formation abilities of A549 cells with ectopic LKB1 and/or NEDD9 expression were assessed in soft agar. Representative photos (B) and the number of colonies (C) are shown. Scale bar, 100 μm (B). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ***, P < 0.001. D and E, representative photos for migration in wounding assay (D) and invasiveness in Matrigel (E) of A549 cells with ectopic LKB1 and/or NEDD9 expression. Scale bar, 200 μm (D) and 40 μm (E). F and G, ectopic NEDD9 expression partially reverses the inhibitory function of LKB1 upon metastasis of A549 cells. Representative photos show the gross metastatic nodules on lung surface (F, indicated by the red arrows) as well as the histology of lung metastasis (G) from nude mice received with A549 cells with ectopic LKB1 and/or NEDD9 expression via tail vein injection. Metastatic incidence is shown on the bottom. Scale bars, 500 μm (top) and 100 μm (bottom).