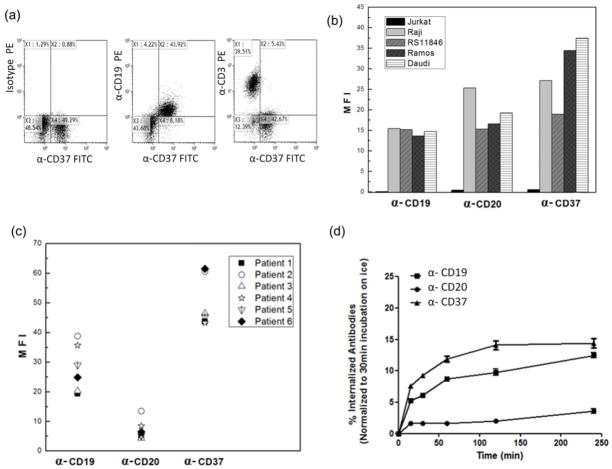
Fig. 2. CD37 is an optimal candidate for targeted delivery to B-CLL cells.
(a) Selective binding of anti-CD37 to CD19+ B cells but not CD3+ T cells in human PBMC. For surface staining, the PBMC cells were incubated with or without anti-CD37-FITC on ice for 30 min and washed twice with cold PBS. Then, the treated cells were further stained with PE labeled anti-CD19 (B-Cell marker) or PE labeled anti-CD3 (T-Cell marker) on ice for another 30 min and rinsed twice with cold PBS. (b) Mean fluorescent intensity of antigen expression levels on cell lines and (c) mean fluorescent intensity of antigen expression levels on CLL patients (n=6). (d) Determination on internalization rates of various mAbs. Cells were incubated with fluorochrome labeled antibodies (anti-CD20-PE, anti-CD19-PE and anti-CD37-PE) at 37°C for 15, 30, 60, 120 and 240 min and extracellular bound antibodies were removed with stripping buffer thus allowing detection of only internalized fluorochrome labeled antibody by flow cytometry. Appropriate IgG isotypes were used as negative controls. Internalization is defined as time-dependent increase in the Mean Fluorescent Intensity (MFI) after acidic washing by stripping buffer, which removed any surface bound antibody (n=3, mean ± SD).