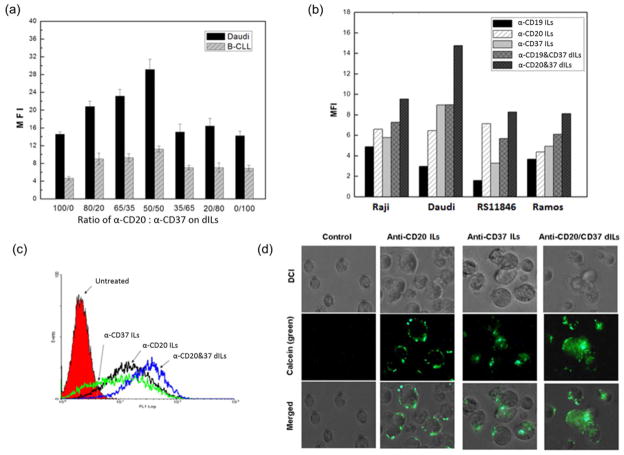
Fig. 4. Optimization of Ab ratio in dILs for efficient delivery to leukemia cell lines and B-CLL cells.
(a) Effect of mAb ratio in dILs on Daudi and B-CLL cells. Indicated ratios of anti-CD20 and anti-CD37 antibodies were immobilized onto liposomes with the post insertion method previously described. The binding efficiency was determined by MFI via flow cytometry detection (n=3, P < 0.0001 for all 100/0 vs. 50/50 or 50/50 vs. 0/100 in Daudi or B-CLL cells). Linear mixed effect models were used to estimate unrestricted covariance structures and produce robust hypothesis tests. Holm’s method was used to adjust for multiplicity. (b) Comparison of delivery efficiency of ILs on B cell lines. Fluorescent labeled ILs were incubated with different cell lines for 30 min followed by twice wash, and MFI were determined by flow cytometry. (c) Histogram comparison of anti-CD20 ILs, anti-CD37 ILs and anti-CD20/anti-CD37 (50/50) dILs. MFI for anti-CD20-ILs, anti-CD37-ILs and anti-CD20/anti-CD37-ILs were 12.3, 13.5 and 18.9, respectively. (d) Confocal microscopy analysis on the enhanced cellular uptake by anti-CD20/anti-CD37 (50/50) dILs compared with the two single-Ab ILs. Cells were incubated with anti-CD20 ILs, anti-CD37 ILs and anti-CD20/anti-CD37 dILs for 4 hrs at 37°C and washed twice with PBS, followed by fixation with 2% paraformaldehyde for 30 min. Anti-CD20/anti-CD37 dILs demonstrated the highest cellular uptake.