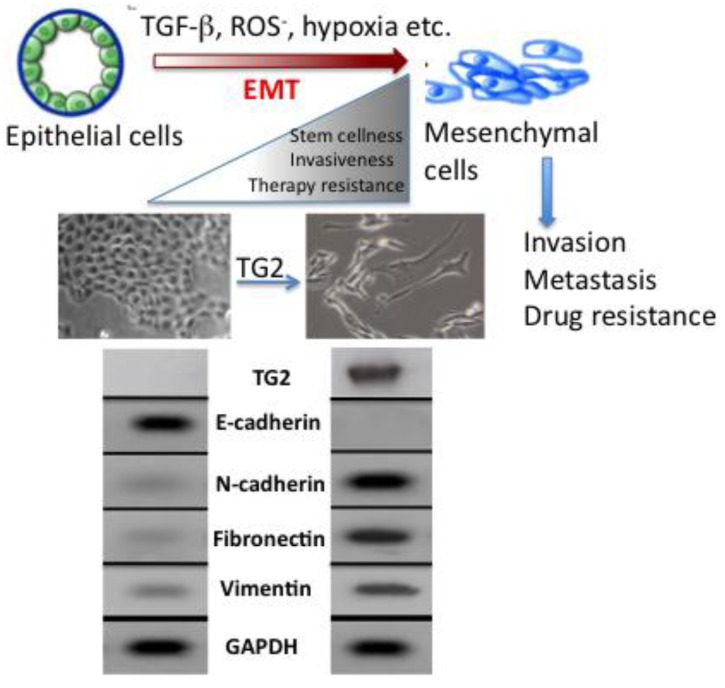
Figure 3.
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) causes functional phenotypic transition of polarized epithelial cells into migratory mesenchymal cells. Stable expression of TG2 induces EMT in epithelial cells (shown here are mammary epithelial MCF10A cells) as revealed by the loss of E-cadherin, upregulation of N-cadherin, fibronectin, and vimentin, anchorage-independent growth, increased invasion, and resistance to doxorubicin [48].