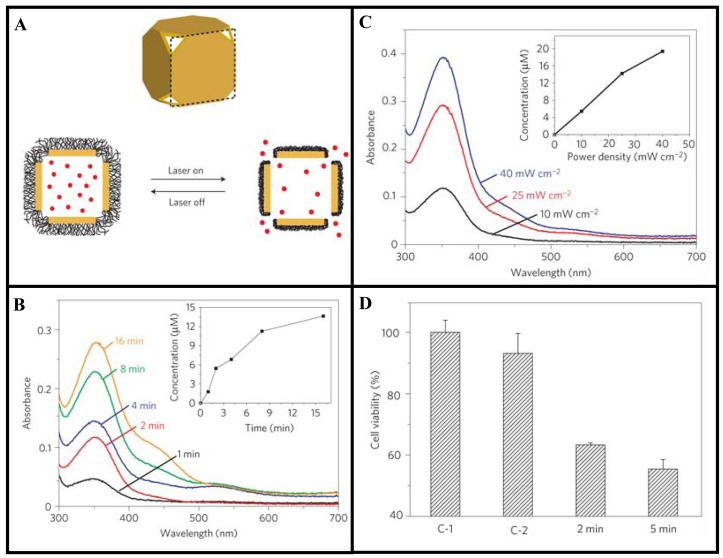
Figure 5.
Use of gold nanocages (GNCs) for drug delivery. (A) Schematic illustrating how the system works. On exposure to a NIR laser, absorbed light is converted into heat, triggering the smart polymer to collapse and thus release the drug. When the laser is turned off, the polymer chains will relax back to the extended conformation and terminate the release. (B) Proof of concept: Absorption spectra of dye, dalizarin-PEG, released from the GNCs after exposure to a laser for different time intervals. (C) Controlled release of an anticancer drug, Dox, from the GNCs. (D) Cell viability after different treatments: (C-1) cells irradiated with a laser for 2 min in the absence of GNCs; (C-2) cells irradiated with the laser for 2 min in the presence of drug-free GNCs; and (2/5 min) cells irradiated with the laser for 2 and 5 min in the presence of drug-loaded GNCs. The power densities used for C-E are 40, 20, and 20 mWcm−2, respectively. The concentration of GNCs was 0.5 nM. Reproduced with permission [15].