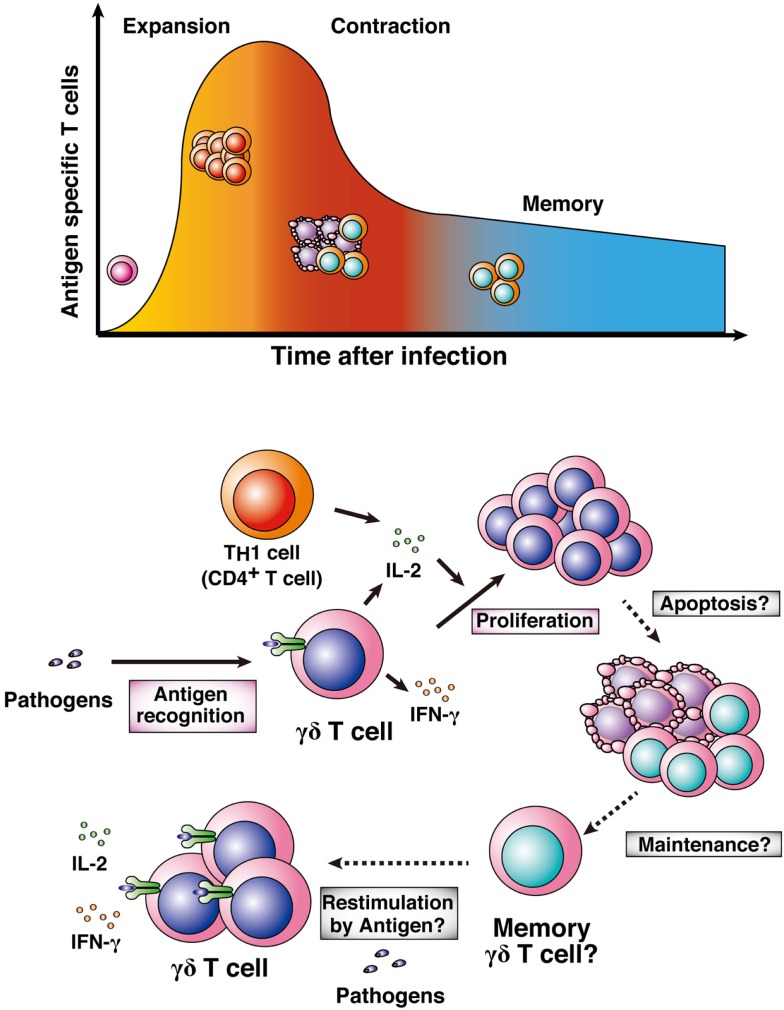
Figure 4.
Memory γδ T cells. Naïve T cells are activated by pathologic infections and differentiate into effector or killer T cells. Activated T cells clonally expand in response to particular antigens (expansion phase). After pathogen clearance, high proportions of the expanded antigen-specific T cells undergo apoptosis (contraction phase). Some population of the surviving antigen-specific T cells is maintained as memory T cells (memory phase). γδ T cells also expand after infection with pathogens, including Plasmodium parasites. High-level proliferation of γδ T cells is involved in generating IL-2 from TH1 cells or the γδ T cells themselves. It remains to be determined whether antigen-specific γδ T cells shift into a contraction phase and then a memory phase.