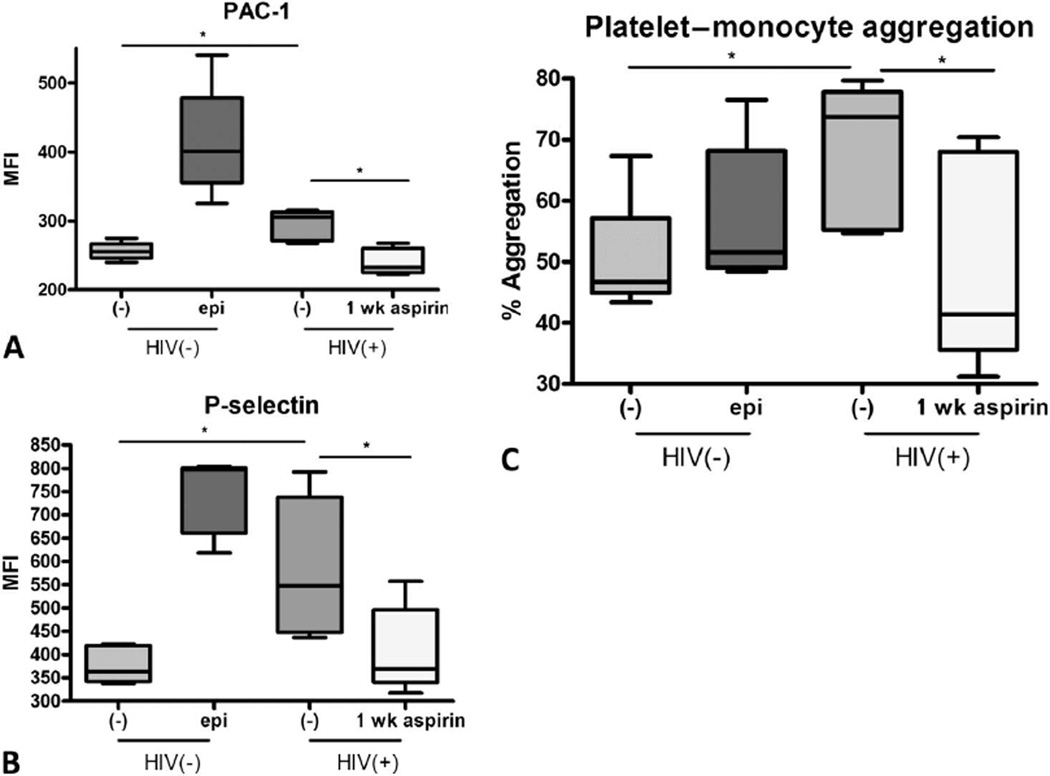
FIGURE 4.
Plasma from HIV-infected subjects activates platelets and HIV-1 plasma–activated platelets activate monocytes. Normal platelets from 5 donors were incubated with control plasma at 37°C for 30 minutes 6 epinephrine or plasma from 5 donor HIV study subjects before and after 1-week aspirin therapy. Normal platelets mixed with plasma from HIV subjects expressed higher platelet activation markers. A, PAC-1; and B, P-selectin at baseline, (*P < 0.05, Mann–Whitney test) but this was abrogated when HIV-1 plasma was used from subjects receiving 1 week of aspirin therapy (paired student t test, *P < 0.05). C, These activated platelets caused THP-1 cell line mon-ocytes to activate more, as measured by CD14+CD61+ double-staining aggregates, Mann–Whitney test, *P ≤ 0.05, but this effect was also abrogated after 1-week aspirin therapy (paired student t test, *P < 0.05). epi, epinephrine.