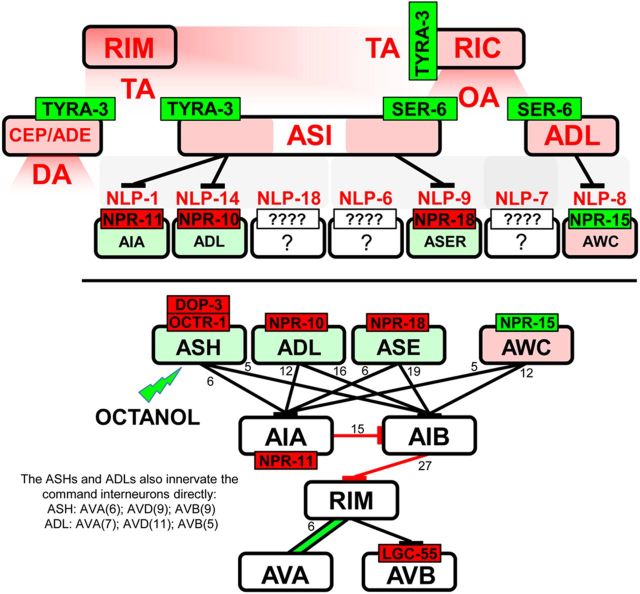
Figure 8.
TA and OA both activate more global signaling cascades to inhibit aversive responses mediated by the ASH sensory neurons. Monoaminergic activation appears to be humoral, whereas peptidergic activation appears to be primarily synaptic. Bottom, Neurons modulated by neuropeptides released from the ASIs and their major connectivities to the locomotory circuit. Red text, Inhibits the 5-HT stimulation of aversive responses to 30% octanol; red receptor, inhibits the neuron; green receptor, stimulates the neuron; red neuron, inhibits 5-HT stimulation; green neuron, stimulates basal aversive responses.