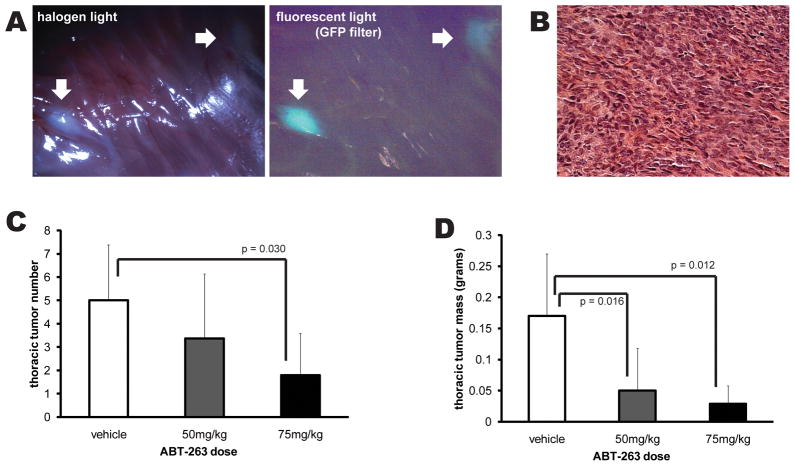
Figure 4. ABT-263 inhibits synovial sarcoma in vivo in a genetic mouse model.
Mice bearing conditional expression of the SS18-SSX2 human cDNA from the Rosa26 locus, activated by Myf5-Cre, develop synovial sarcomas most consistently in the intercostal muscles of the thoracic cage, detectable by 12 weeks of age. (A) Mice treated with intraperitoneal injection of either DMSO or DMSO with ABT-263 for three doses weekly during weeks 13, 14, and 15 of life were euthanized at 15 weeks for visual and GFP-fluorescence assessment of the thoracic cage (white arrows), followed by measurement of the mass of the tumors themselves. (B) Histology confirmed the characteristic synovial sarcoma appearance of each mass counted and weighed. (C) Treatment of mice with 75mg/kg/dose (n = 5) of ABT-263 decreased the total number of thoracic cage masses identified (by Student’s t-test). (D) Treatment with either 50mg/kg/dose (n=8) or the higher dose resulted in statistically significant reduction of total tumor mass compared to vehicle control (n = 7). All experimental mice derived from the same two parents, with controls and treatment mice in each of the three litters used. All results are presented as means with standard deviation error bars.