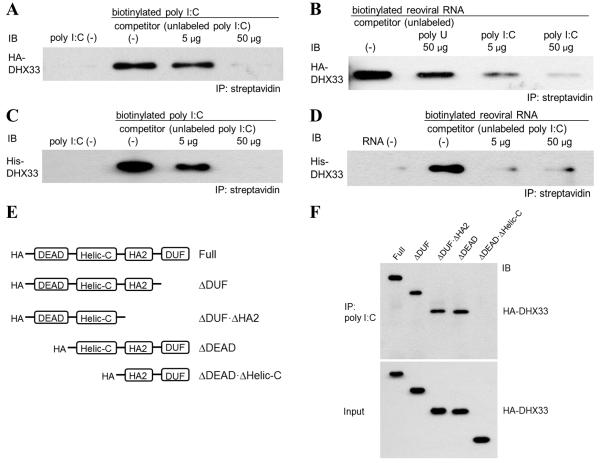
Figure 4. DHX33 requires the helicase C domain for binding to dsRNA.
(A and B) HA-DHX33 was overexpressed in HEK293T cells and purified by anti-HA beads. Purified HA-DHX33 protein was incubated with biotinylated poly I:C (A) or biotinylated genomic reoviral RNA (B) in the absence (0 μg) or presence (A: 5 or 50 μg of poly I:C; B: 50 μg of poly U, 5 or 50 μg of poly I:C) of unlabeled competitor. Biotinylated poly I:C (A) or reoviral RNA (B) was precipitated by streptavidin beads, followed by immunoblotting (IB) for HA-DHX33.
(C and D) Recombinant His-DHX33, generated in E. coli, was incubated with biotinylated poly I:C (C) or biotinylated reoviral genomic RNA (D) in the absence (0 μg) or presence (5 or 50 μg) of unlabeled poly I:C as a competitor. Biotinylated dsRNA was immunoprecipitated by streptavidin beads, followed by IB for DHX33.
(E) Purified full-length and truncated HA-DHX33 proteins were incubated individually with biotinylated poly I:C. Biotinylated poly I:C was immunoprecipitated by streptavidin beads, followed by IB for HA-DHX33. DEAD, Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp domain; HELICc, helicase C-terminal domain; HA2, helicase-associated domain 2; DUF, domain of unknown function.
See also Figure S3.