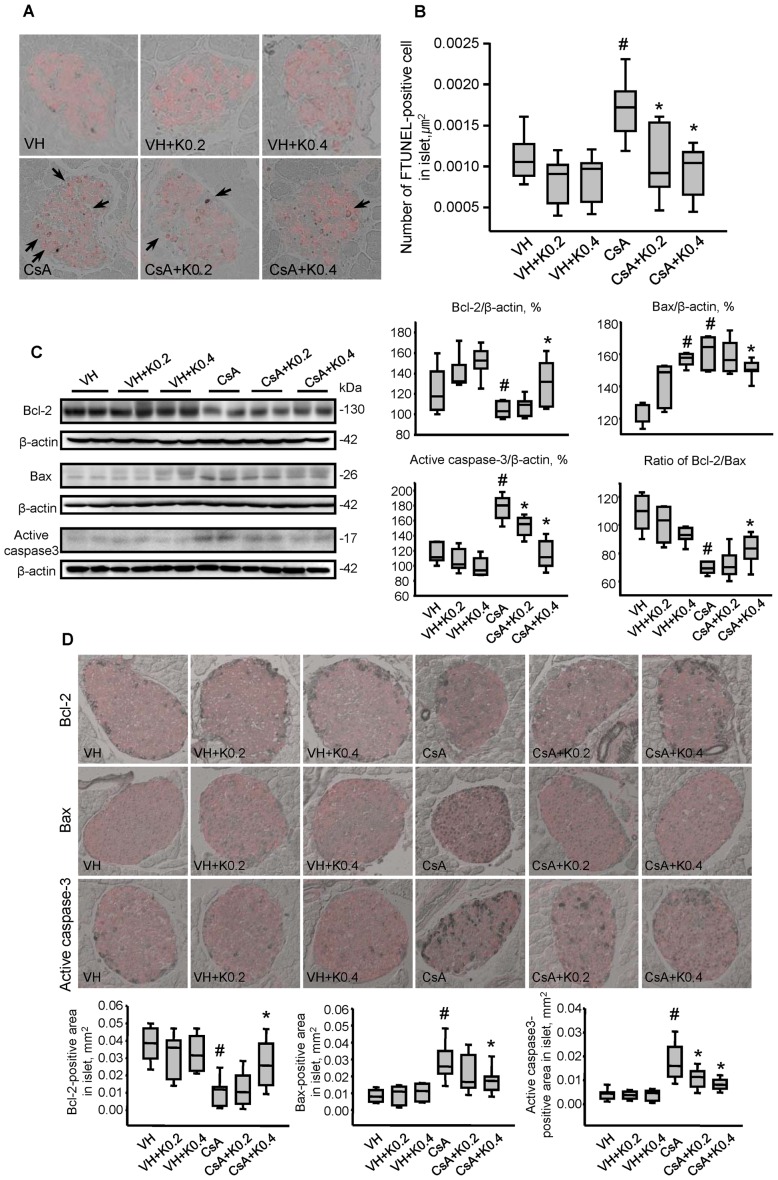
Figure 4. Effect of KRG on apoptotic cell death in CsA-induced pancreatic injury.
(A) TUNEL assay for detecting apoptosis in pancreatic cells identified by immunostaining for insulin in the same tissue sections of the experimental groups. Apoptotic cell death featured condensation and fragmentation of the nucleus and shrinkage of the cells with condensation of the cytoplasm and detachment from the surrounding tissues. TUNEL-positive nuclei were rarely observed in the groups treated with VH only or with VH plus K. However, their numbers increased dramatically in the CsA-treated group, but this increase was attenuated in the CsA plus K0.2 or K0.4 groups. (B) Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive nuclei in the experimental groups. The numbers were reduced significantly in the CsA plus K0.2 or K0.4 groups compared with the CsA-only group. (C) Quantitative analysis of Bcl-2, Bax and active caspase-3 using immunoblotting of whole pancreatic tissues from the experimental groups. The expression level of Bcl-2, an antiapoptotic marker, was significantly reduced in the CsA plus K0.2 or K0.4 groups compared with the CsA-only group. By contrast, the expression levels of Bax and active caspase-3, proapoptotic markers, were reduced in the CsA plus K0.4 group compared with the CsA-only group. (D) Representative photomicrographs showing double immunolabeling for insulin (red) and Bcl-2 or Bax or active caspase-3 (gray) in pancreatic cells in the same tissue sections from the experimental groups. As in whole pancreatic tissues, quantitative analysis results showed that the immunoreactivity of Bcl-2 was decreased in the CsA group, but this decrease recovered markedly with KRG cotreatment. Bax and active caspase-3 levels were decreased in the CsA plus K-treated groups compared with the CsA group. Values are SE (n = 10). Relative optical densities of bands in each lane were normalized with each β-actin band from the same gel. Magnifications×400. #P<0.05 vs. VH; *P<0.05 vs. CsA.