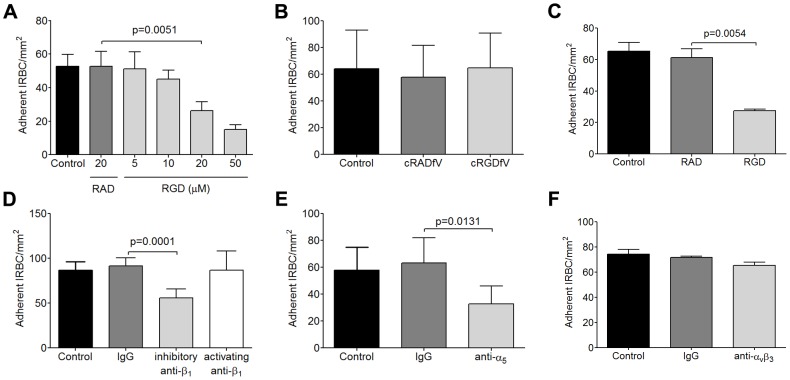
Figure 1. Inhibition of cytoadherence on HDMEC by RGD peptide and anti-b1 and anti-a5 mAb.
(A) Adhesion of IRBC to endothelial monolayers pre-incubated with 20 µM RAD or 5–50 µM RGD peptide for 30 min at 37°C in 5% CO2. A 1% hematoctit suspension of IRBC from the lab-adapted parasite clone 7G8 was drawn over the monolayers at 1 dyne/cm2. Results shown are the mean number of adherent IRBC/mm2 in 4–6 microscopic fields (20×) after 7 min of infusion (n = 6). (B) Adhesion of 7G8 parasites to endothelial monolayers pre-incubated with 20 µM cRADfV or cRGDfV peptide (n = 3). (C) Adhesion of 3 clinical parasite isolates to endothelial monolayers pre-incubated with 20 µM RAD or RGD peptide (n = 10 for 3 clinical isolates each tested in 3 to 4 independent experiments). (D) Adhesion of clinical isolates to endothelial monolayers pre-incubated with control IgG1, an inhibitory anti-β1 integrin mAb TDM29 or the activating anti-β1 integrin mAb TS2/16 at 10 mg/ml (n = 3 for 3 clinical isolates each tested in 1 independent experiment). (E) Adhesion of clinical isolates to endothelial monolayers pre-incubated with control IgG1, and an inhibitory anti-α5 integrin mAb JBS5 at 10 µg/ml (n = 3 for 3 clinical isolates each tested in 1 independent experiment). (F) Adhesion of clinical isolates to endothelial monolayers pre-incubated with control IgG1, and an inhibitory anti-αvβ3 integrin mAb 23C6 at 10 µg/ml (n = 3 for 3 clinical isolates each tested in 1 independent experiment).