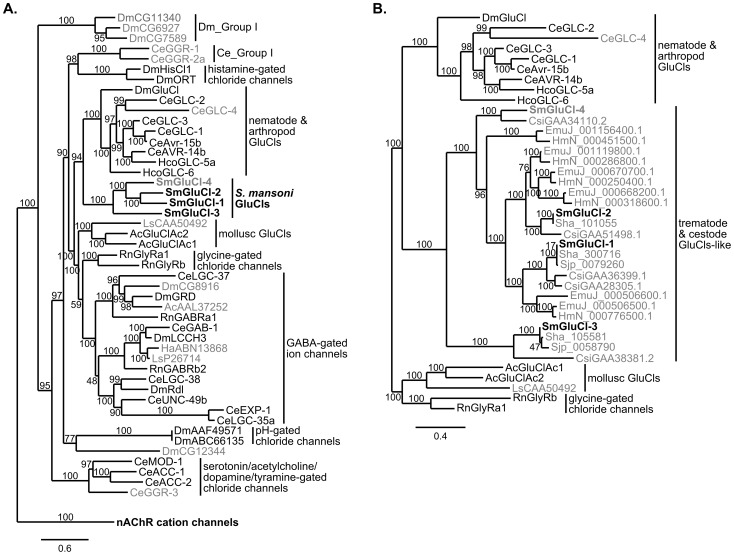
Figure 6. Phylogenetic relationship between the SmGluCl subunits and the inhibitory Cys-loop LGIC family.
Maximum likelihood tree showing the evolutionary relationship of S. mansoni GluCl subunits compared to other Cys-loop anionic LGIC subunits. A. SmGluCl-1, SmGluCl-2, SmGluCl-3 and SmGluCl-4 subunits belong to an independent glutamate-gated chloride channel clade evolutionarily distinct from their mollusc, arthropod and nematode counterparts. No schistosome Cys-loop LGIC subunits are predicted to mediate GABA signaling. All other LGIC subunits predicted from S. mansoni genome belong to the nAChR cation channel family (not shown). The phylogenetic analysis included inhibitory Cys-loop LGIC subunits from Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), Haemonchus contortus (Hco), the snail species Aplysia californica (Ac), Haliotis asinina (Ha) and Lymnaea stagnalis (Ls), and Rattus norvegicus (Rn). The cation-selective GABA-gated channel subunits CeEXP-1, CeLGC-35, DmGRD and DmLCCH3 were included as part of the inhibitory Cys-loop LGIC family. The tree was rooted using C. elegans nAChR cation channel subunits ACR-11, DEG-3, UNC-29 and UNC-38 as outlier. B. SmGluCl-1, SmGluCl-2, SmGluCl-3 and SmGluCl-4 subunits belong to the flatworm GluCl subunit clade that includes other trematode and cestode putative GluCl-like subunits. The flatworm GluCl family is evolutionarily distinct from the mollusc, arthropod and nematode GluCl families. The phylogenetic analysis included the GluCl and GlyR subunits from panel A, as well as GluCl-like subunits from the trematode S. japonicum (Sjp), S. haematobium (Sha) and C. sinensis (Csi), and the cestodes E. multilocularis (EmuJ) and H. microstoma (HmN). For both trees, subunits for which the function had not been confirmed by heterologous expression are labeled in gray. S. mansoni GluCl subunits are in bold. Amino acid sequences were aligned with PROMALS3D and non-alignable, non-informative sites were removed manually. The Phylogeny.fr platform was used for tree building (PhyML v3.0, WAG substitution model). Numbers on internal branches indicate reliability (%) for internal branches and were assessed using the aLRT test (Chi2-based parametric).