Fig. 3.
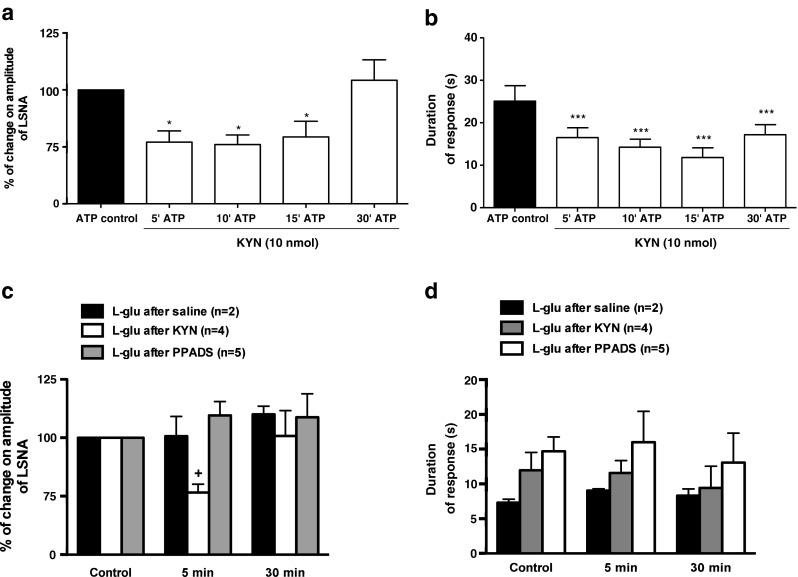
Effects of P2 receptors antagonism (PPADS) or ionotropic glutamatergic receptors antagonism (KYN) on the sympathoexcitation induced by ATP or L-glu microinjected into the PVN. a and b KYN (10 nmol) previously microinjected into the PVN was able to attenuate the percentage of increase on amplitude of LSNA and b the duration of response (onset until recovery to baseline), respectively, induced by ATP (2.5 nmol) microinjection at the same level. c and d Previous antagonism of ionotropic glutamate receptors with KYN (10 nmol), but not P2 receptors (PPADS 0.5 nmol), within the PVN elicits significant attenuation on the amplitude of LSNA and the duration of response (onset until recovery to baseline), respectively, induced by L-glutamate (1 nmol) at the same site. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.01 compared to control vs. ATP in the presence of KYN; +p < 0.05 compared to control and saline at the same time course. One-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test
