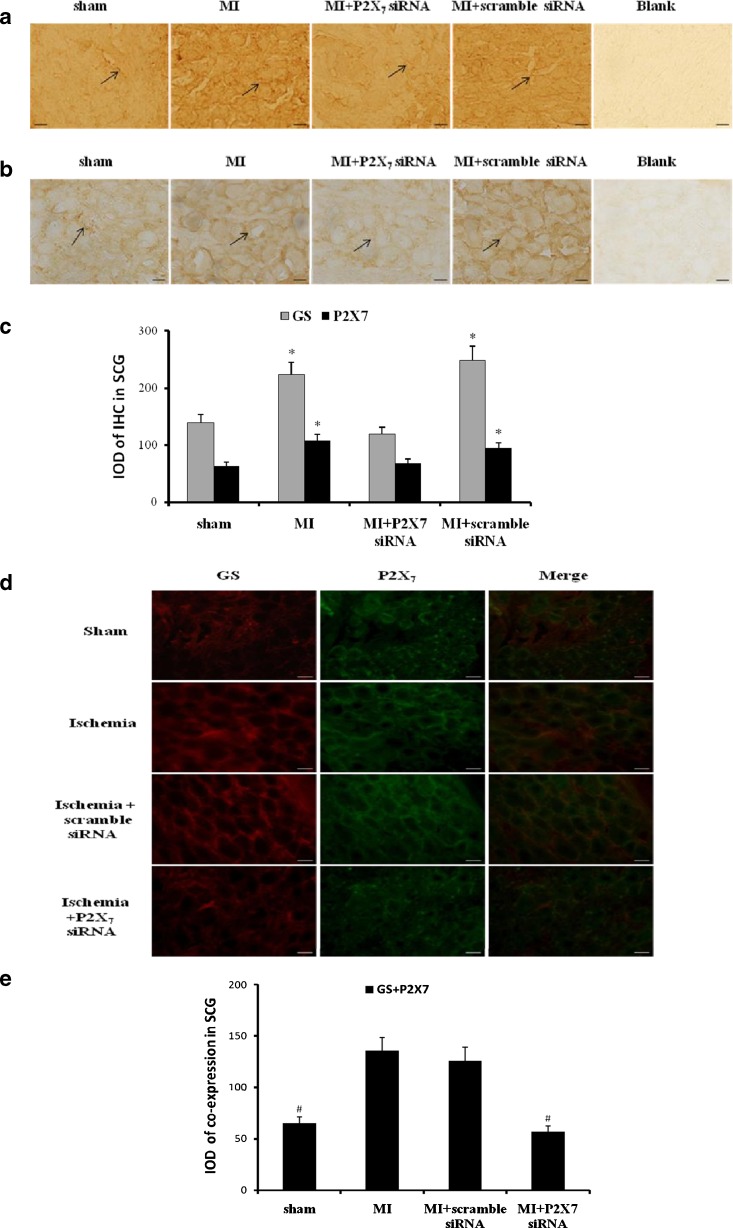
Fig. 5.
Effects of siRNA P2X7 on the expression or co-expression of P2X7 or/and GS in SCG. The expressions of P2X7 (a) or GS (b) were assessed by immunohistochemistry. After siRNA P2X7 in myocardial ischemic rats, the expression levels of GS or P2X7 were significantly lower than those in MI group and MI+scramble siRNA group (n = 6, respectively; p < 0.05). There was no significant difference among sham group and MI+P2X7 siRNA group (n = 6, respectively; p > 0.05). Arrows indicate the immunostaining neurons. Scale bars, 20 μm. The bar graphs (c) showed the statistical results for expression of GS or P2X7 immunoactivity. Results are mean ± SE. *p < 0.05 vs sham group, con+oxATP group, and MI+oxATP group. The co-expression of GS and P2X7 receptor in SCG was measured by double-label immunofluorescence after siRNA P2X7 receptor (d). After siRNA P2X7 in myocardial ischemic rats, the co-expression staining of GS and P2X7 was significantly lower than that in MI group and MI+scramble siRNA group (n = 6, respectively; p < 0.05). There was no significant difference among sham group and MI+P2X7 siRNA group (n = 6, respectively; p > 0.05). The results further revealed that P2X7 receptor was involved in myocardial ischemic injury. Red signal represents GS staining with TRITC, and green signal indicates P2X7 staining with FITC. Merge represents GS and P2X7 double staining image. Scale bar, 20 μm. The bar graphs showed the statistical results for co-expression of GS and P2X7 in SCG (e)