FIGURE 5.
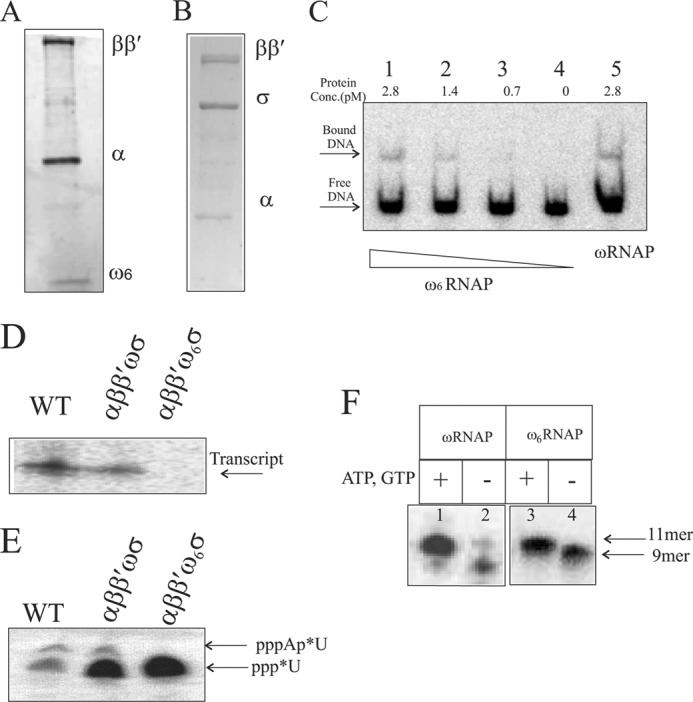
In vitro reconstitution and transcription activity of the ω6-bearing RNAP holoenzyme. Shown are the subunit compositions of reconstituted core RNAP with ω6 on 8–20% gradient SDS-PAGE (A) and reconstituted holo-RNAP with ω6 on10% SDS-PAGE (B). C, promoter DNA-polymerase complex formation. Lanes 1–4 show the indicated concentration of reconstituted ω6RNAP forming a heparin-resistant DNA-protein complex; lane 5 shows the complex formed by reconstituted wild-type polymerase. The free DNA and DNA-protein complex are marked with arrows. D, T7A1 promoter-specific in vitro single round transcription assay generating transcript with purified RNAP holoenzyme isolated from cells (WT) and holoenzyme versions of reconstituted ωRNAP and ω6RNAP. Enzyme and promoter concentrations used are 2 and 0.2 pmol, respectively. E, abortive transcription assay detecting first phosphodiester bond formation by 20% urea-PAGE. F, transcription activity of ωRNAP/ω6RNAP on preformed elongation complex with synthetic coding strand and 9-mer RNA primer along with bound enzyme. Lanes 1 and 3, with additional nucleotide added forming 11-mer transcript; lanes 2 and 4, no addition of nucleotide showing 9-mer RNA primer in elongation complex with template DNA strand and bound enzyme.
