FIGURE 9.
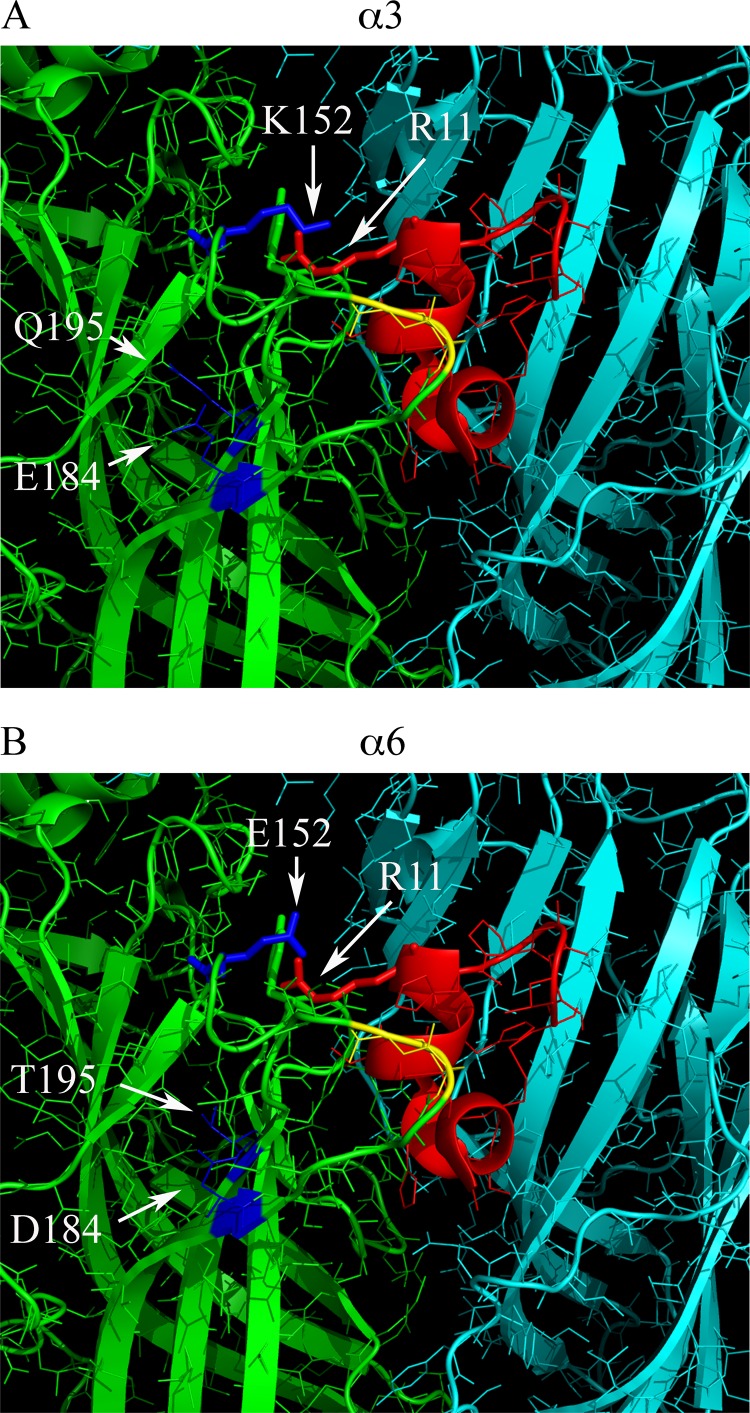
Homology binding model of PeIA(A7V,S9H,V10A,N11R,E14A) to rat α3β2 and α6β2 nAChRs. A, a 20 Å radius view of the ACh binding pocket of the A. californica AChBP complexed with α-Ctx PnIA(A10L,D14K) The principal subunit is shown in green, and the complementary subunit is shown in cyan. Residues 147–153 of the B-loop and 185–195 of the C-loop of the principal binding subunit were mutated to the homologous residues found in the rat α3 subunit. Residues of the C-loop shown in yellow are Cys189 and Cys190, and the residues shown in blue are Glu184 and Gln195 of the C-loop, and Lys152 of the B-loop, shown as a stick model. Residues of PnIA(A10L,D14K) were mutated to those of PeIA(A7V,S9H,V10A,N11R,E14A) and shown in red with Arg11 shown as a stick model. Note the close proximity of Lys152 of the α3 subunit and Arg11 of the α-Ctx, suggesting a possible interaction between the two. B, residues 147–153 of the B-loop and 185–195 of the C-loop of the AChBP principal binding subunit were mutated to the homologous residues found in the rat α6 subunit. Residues in blue are Asp184 and Thr195 of the C-loop and Glu152 of the B-loop. Mutagenesis of the AChBP and α-Ctx PnIA(A10L,D14K) as well as image rendering were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.”
