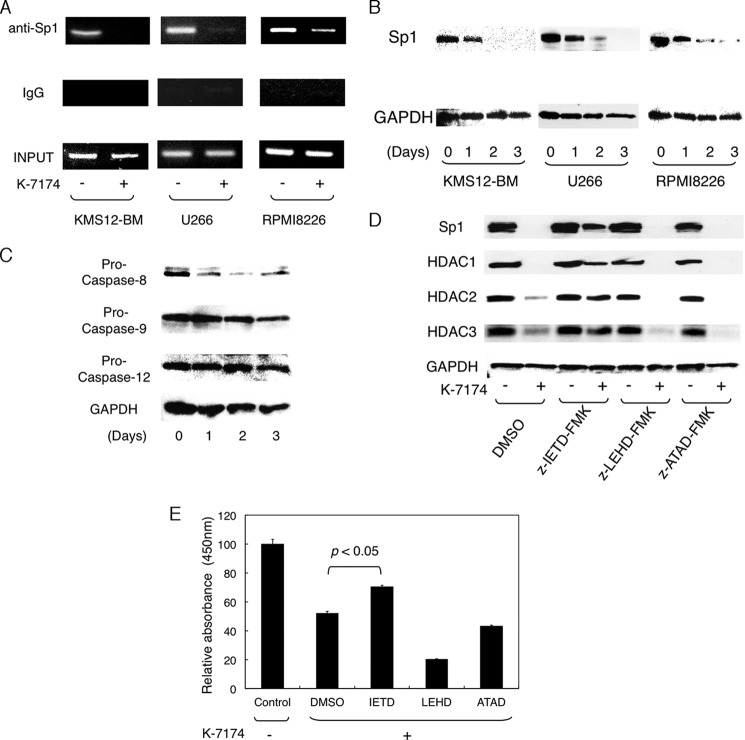
FIGURE 5.
K-7174 induces transcriptional repression of class I HDAC genes via caspase-8-mediated degradation of Sp1. A, MM cell lines were cultured with either K-7174 (+) or vehicle control (−) for 2 days, and subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. Chromatin suspensions were immunoprecipitated with anti-Sp1 and isotype-matched (IgG) antibodies. The resulting precipitants were subjected to PCR to amplify the promoter regions of the HDAC1 gene as described previously (21). The amplified products were visualized by ethidium bromide staining after 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Representative data of 50 cycles are shown. Input indicates that PCR was performed with genomic DNA. B, MM cell lines were cultured with K-7174 (5 μm for U266 and 10 μm for KMS12-BM and RPMI8226) for up to 3 days. Whole cell lysates were prepared at the given time points and subjected to immunoblotting for Sp1 and GAPDH (internal control). C, RPMI8226 cells were cultured with 10 μm K-7174 for up to 3 days. Whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting for pro-caspase-8, -9, and -12 and GAPDH (internal control). D, RPMI8226 cells were cultured with 100 μm Z-IETD-fmk (caspase-8 inhibitor), 100 μm Z-LEHD-fmk (caspase-9 inhibitor), 20 μm Z-ATAD-fmk (caspase-12 inhibitor), or vehicle alone (DMSO) for 48 h in the absence or presence of 10 μm K-7174. Whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting for Sp1, HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, and GAPDH (internal control). E, cell viability was determined after culturing RPMI8226 cells in the absence (Control) or presence of 10 μm K-7174 with 100 μm Z-IETD-fmk (IETD), 100 μm Z-LEHD-fmk (LEHD), 20 μm Z-ATAD-fmk (ATAD), or the vehicle control (DMSO) for 72 h. Absorbance at 450 nm was measured with a microplate reader, and expressed as a percentage of the value of the corresponding control cells. The mean ± S.D. (bars) of three independent experiments are shown. p values were calculated by one-way analysis of variance with the Student-Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons test.