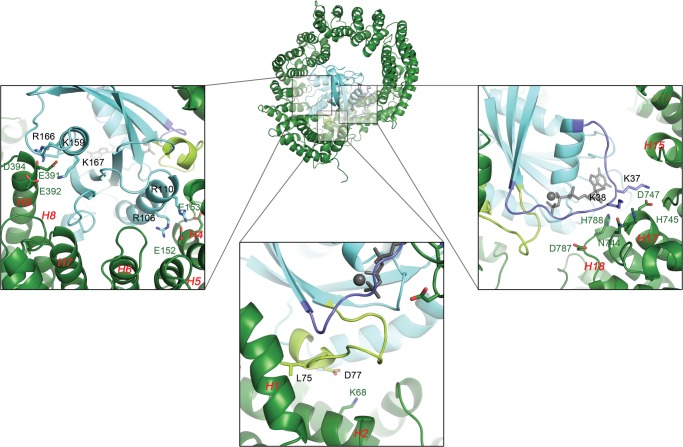
FIGURE 7.
Interactions between RanGTP and TRN-SR2 predicted by homology modeling. The central image shows a graphic representation of the TRN-SR2-RanGTP complex. The lower panels zoom in on the three main interaction sites between both proteins. Main interacting amino acids are rendered as sticks and are labeled in the color of the corresponding protein/region. HEAT repeats are labeled in red, and the Ran switch I and II regions (amino acids 32–45 and 66–80) are colored purple and pale green, respectively. On the left the interaction interface in the middle of TRN-SR2 is displayed. An acidic stretch in the TRN-SR2 HEAT 9 repeat containing Glu-391, Glu-392, and Asp-394 allows formation of salt bridges with RanGTP residues Lys-159, Arg-166, and Lys-167. Similarly, two arginines from RanGTP (Arg-106, Arg-110) balance the charges of two glutamic acid residues (Glu-152, Glu-153) in the HEAT 4 B-helix. These last two residues lie next to the interface TRN-SR2 makes with the Ran switch II region, depicted in the middle panel. Here another salt bridge is established between the HEAT 2 B-helix Lys-68 and a Asp-77 counterpart in the switch. Additionally, Leu-74 from switch II inserts its hydrophobic side chain into a shallow pocket formed between the HEAT 1 and 2 B-helices. On the right is the interface of the RanGTP switch I region with HEAT repeats 16–19. Main interactions are again polar in nature as residues Lys-37 and Lys-38 from the switch reach out to a patch containing TRN-SR2 residues Asn-744, His-745, and Asp-747 on HEAT 17 and Asp-787 and His-788 on HEAT 18.