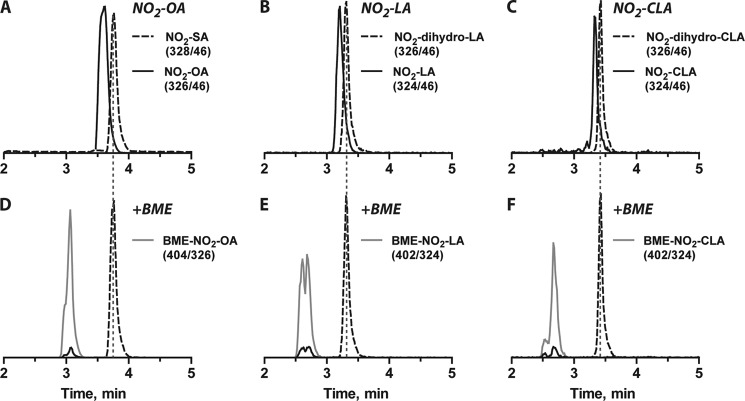
FIGURE 3.
Analysis of the electrophilic reactivity of nitro fatty acid derivatives. A–C, shown are representative LC-MS/MS peaks for both native (continuous lines) and reduced forms (dashed lines) of NO2-OA (A), NO2-LA (B), and NO2-CLA (C). D–F, incubation with β-mercaptoethanol (BME) leads to the disappearance of peaks corresponding to the electrophilic NO2-OA (D), NO2-LA (E), and NO2-CLA (F) species, whereas no reaction was observed with the enzymatic reduction products. Early-eluting peaks corresponding to transitions associated with the unsaturated nitroalkenes reflect in-source fragmentation of the β-mercaptoethanol adducts. The gray continuous lines show the appearance of the expected Michael adducts formed upon reaction of β-mercaptoethanol with the corresponding nitroalkenes. Nitroalkenes were incubated with 7.3 μg/ml enzyme-enriched fraction for 1 h at 37 °C, and electrophilicity was assessed as described under “Experimental Procedures.”