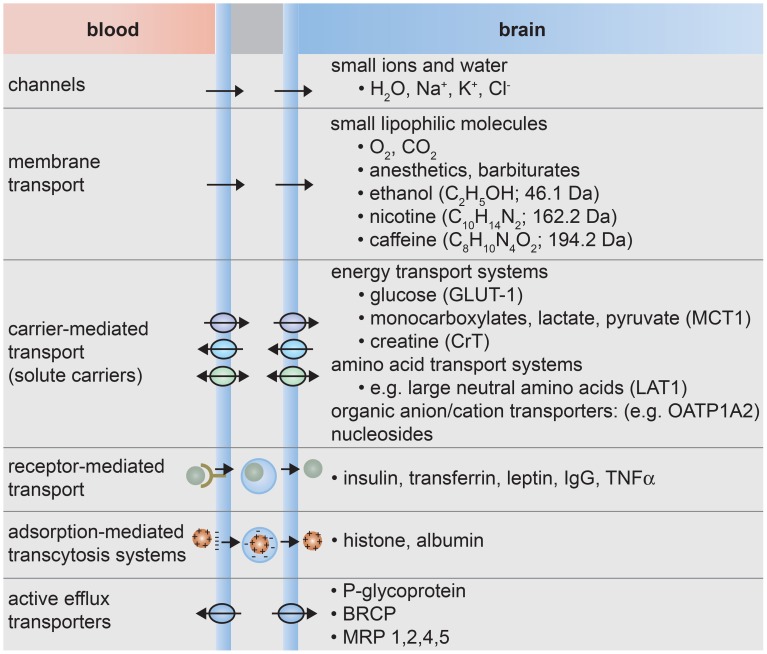
Figure 3.
Transport systems at the blood-brain barrier. (1) Small ions and water molecules can cross the blood-brain barrier through ion channels. (2) Small lipophilic molecules that are soluble in the hydrophobic core of the cell membrane can be transported passively across the cell. (3) Essential polar molecules that cannot diffuse through the cell membrane are shuttled across the cell membranes by carrier-mediated transport. These solute carriers may be directional, in or out of the cell, or bidirectional. Other molecules can be actively transported across endothelial cell membranes by carrier-mediated transporters, receptor-mediated transporters, adsorption-mediated transcytosis, or efflux pumps.