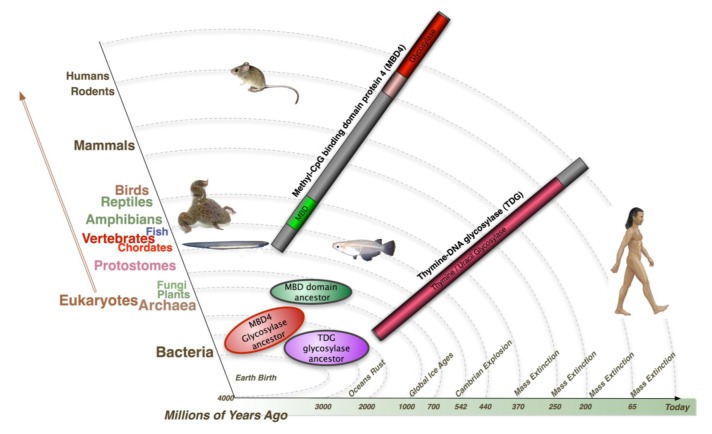
Figure 4.
Evolutionary timeline of the two mammalian Thymine glycosylase proteins: Methyl-CpG binding domain protein 4 and Thymine-DNA glycosylase (TDG). The ortholog of proteins including the MBD domain and the glycosylase domain of human MBD4 and of full length human TDG were inferred initially by reciprocal best BLASTP searches against the non-redundant protein sequences database, and confirmed by phylogenetic reconstructions. Neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic trees were constructed for domains of MBD4 and full length TDG proteins. Maximum likelihood (ML) analyses were performed using the PHYML module from Geneious pro software, following the JTT model of amino acid substitution. Protein domains were identified using InterProScan and Conserved Domains servers. Published procedures for this bioinformatic approach were followed [99]. Both glycosylase ancestors of MBD4 and TDG were found in Bacteria. Glycosylase ancestors of MBD4 were found in Archaea, whereas only a hypothetical TDG Archaea ortholog was identified. Both glycosylase ancestors of MBD4 and TDG were found in Plants and Fungi, in contrast, the earliest MBD domain ancestors were in plants and not in Fungi. TDG protein was found in almost all the species throughout evolution, the full length MBD4 though, emerges as a fusion protein only from Chordates: the representative of Invertebrate-Vertebrate transition.