Figure 4.
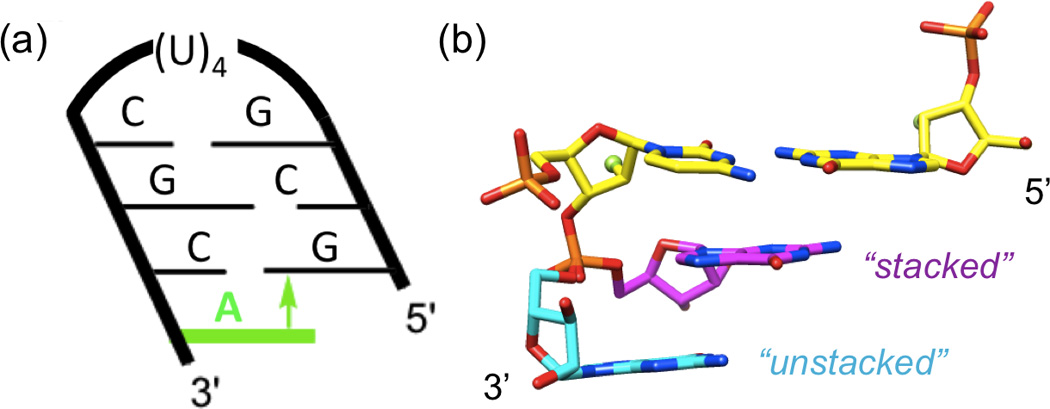
(a) Hairpin construct used to assess the contribution of base stacking to the relative stabilities of 2'-F RNA and RNA. The negative inclination between backbone and base pairs in 2'-F RNA and RNA results in considerable cross-strand stacking[23,24] and a stabilizing π-π interaction (arrow) between the 3'-overhanging A (green) and the 5'-terminal G. (b) Dual conformations of a 3'-terminal G in the crystal structure of a mixed 2'-F/2'-OH RNA duplex (PDB ID 3P4C),[9] unstacked (cyan carbons) and stacked (magenta carbons) onto the terminal C:G pair (yellow carbons). F2'/O2' atoms of the terminal pair are highlighted as green spheres. Neither conformation of G features an intra-nucleoside H-bond involving the 2'-OH moiety.
