Figure 1.
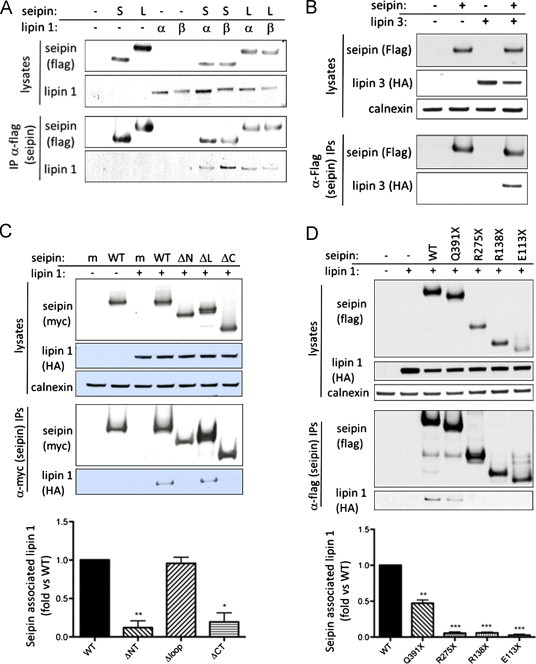
Seipin binds to lipin 1 via its C terminus. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with empty vector (–) or Flag-tagged short form (S) or long form (L) of seipin in the presence or absence of HA-tagged lipin 1α (α) or lipin 1β (β). Lysates or anti-Flag immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS PAGE and blotted for Flag or Lipin 1. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with empty vector (–) or Flag-tagged long form of seipin in the presence or absence of HA-tagged lipin 3 as indicated. Lysates or anti-Flag immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS PAGE and blotted for Flag or HA. (C) HEK293 cells were transfected with wild-type myc-seipin (WT) or mutants lacking the N-terminus (ΔNT), the ER lumenal loop region (ΔLP) or the C-terminus (ΔCT) in the absence or presence of Lipin 1β as indicated. Lysates or anti-myc immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS PAGE and western blotted for myc, HA and calnexin. (D) HEK293 cells were co-transfected with wild-type Flag-seipin or Flag-seipin where pathogenic mutations had been introduced to generate Q391X, R275X, R138X or E113X premature stop mutants of the protein. Lysates or anti-flag immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS PAGE and western blotted for flag, HA and calnexin. In both (C) and (D) quantification of Lipin 1β co-immunoprecipitating with wild-type and mutant forms of myc-seipin as in (C). Data are means±SEM, n=4 (C) or n=3 (D). * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01, *** indicates p<0.001 versus co-immunoprecipitation with wild-type seipin.
