Fig. 2.
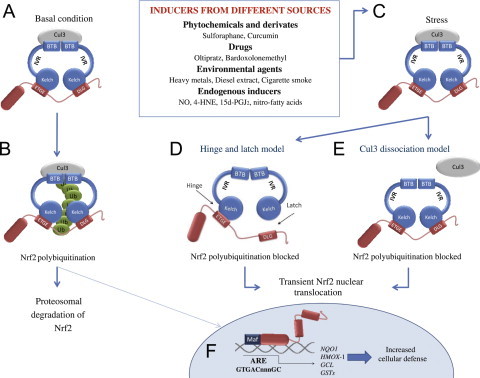
The Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. (A and B) in basal conditions, two Keap1 molecules bind to Nrf2 and Nrf2 is polyubiquitylated by the Cul3-based E3 ligase complex. This polyubiquitilation results in rapid Nrf2 degradation by the proteasome. A small proportion of Nrf2 escapes the inhibitory complex and accumulates in the nucleus to mediate basal ARE-dependent gene expression, thereby maintaining the cellular homeostasis. (C) Under stress conditions, inducers modify the Keap1 cysteines leading to the inhibition of Nrf2 ubiquitylation via dissociation of the inhibitory complex. (D) According to the hinge and latch model, modification of specific Keap1 cysteine residues leads to conformational changes in Keap1 resulting in the detachment of the Nrf2 DLG motif from Keap1. Ubiquitination of Nrf2 is disrupted but the binding with the ETGE motif remains. (E) In the Keap1-Cul3 dissociation model, the binding of Keap1 and Cul3 is disrupted in response to electrophiles, leading to the escape of Nrf2 from the ubiquitination system. In both of the suggested models, the inducer-modified and Nrf2-bound Keap1 is inactivated and, consequently, newly synthesized Nrf2 proteins bypass Keap1 and translocate into the nucleus, bind to the Antioxidant Response Element (ARE) and drive the expression of Nrf2 target genes such as NQO1, HMOX1, GCL and GSTs [1,3].
