Fig. 1.
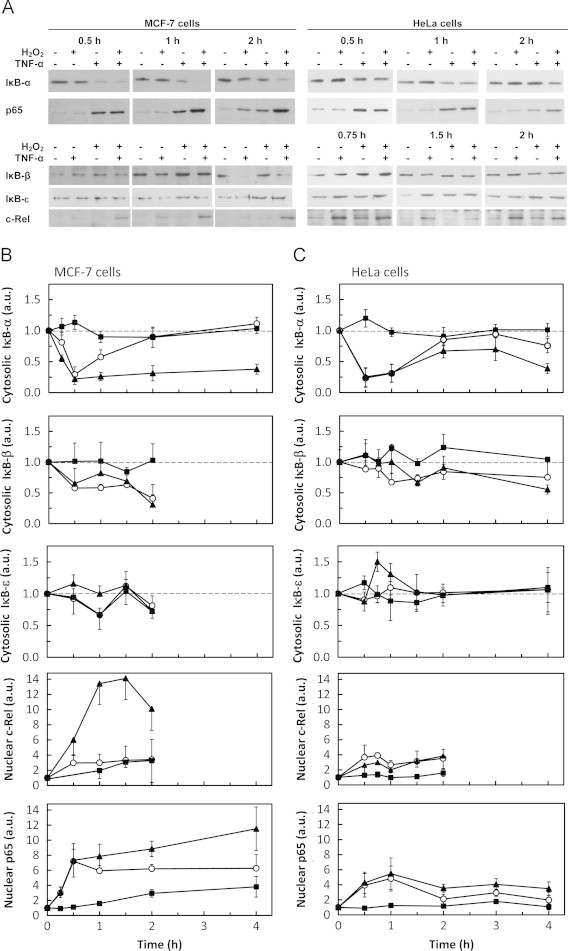
Differential modulation of IκB and Rel proteins by H2O2 and TNF-α. The levels of cytosolic IκB-α, IκB-β and IκB-ε and of nuclear p65 and c-Rel were followed by western blot. (A) Representative immunoblots of n=3–8 independent experiments showing the effect of H2O2 and TNF-α on IκB-α, IκB-β, IκB-ε, p65 and c-Rel. Signal intensity quantification of protein levels expressed as the mean±standard deviation in arbitrary units (a.u.) relative to control for MCF-7 cells (B) and HeLa (C) cells exposed to either steady-state 25 µM H2O2 (■) or 0.37 ng mL−1 TNF-α (○) or both agents simultaneously (▲). Protein levels were normalized to the protein loading (membrane stained with Ponceau S). In order to make the figure easier to analyze, the protein loading controls are only shown as supplementary information (Supplementary Fig. S1). In MCF-7 cells, the values for c-Rel are a minimal value because no band was observed in control cells and normalization was made with the lighter band visualized in the immunoblot. Statistically significant differences found for data represented in Fig. 1 are only referred in the text.
