Figure 4.
Genetic Ablation of Sox2 in Adult Mice Causes Aberrant Skin Repair Concomitantly with Deficits in the NCPC Injury Response
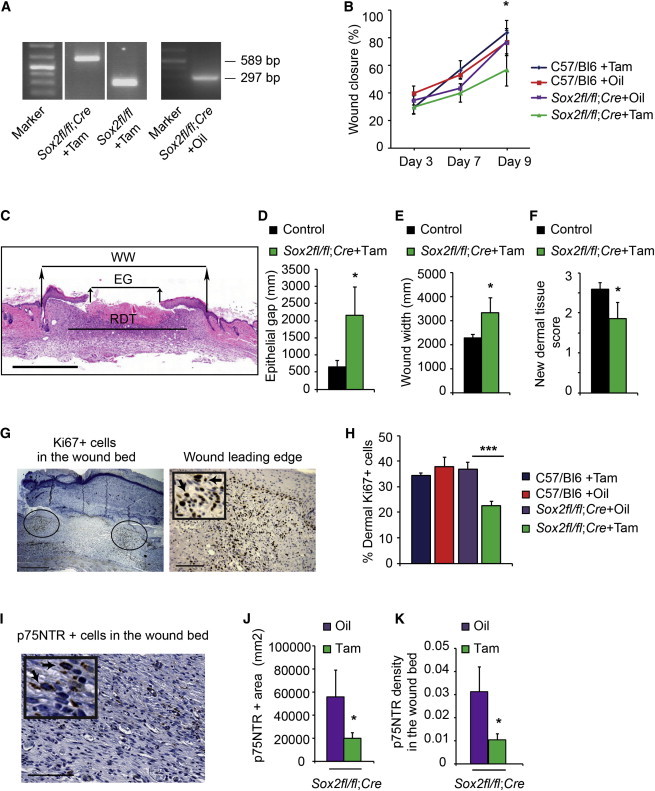
(A–K) Sox2fl/fl;R26CreERT2/+ mice were treated with tamoxifen (Sox2fl/fl;Cre+Tam, n = 7) or vehicle (Sox2fl/fl;Cre+Oil, n = 6) at 9 months, and punch wounds were performed 5 weeks later. As additional controls, wild-type mice of the same genetic background were treated with tamoxifen (C57/Bl6+Tam, n = 7) or oil (C57/Bl6+Oil, n = 5).
(A) Genomic DNA PCR analysis showing the 297 nt product from the intact floxed allele, and the 589 nt product generated from the floxed allele after Cre-mediated recombination.
(B) Extent of wound closure 3–9 days postinjury. Two-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05 for group effect.
(C) Representative hematoxylin-and-eosin-stained section through the center of the wound bed 9 days postinjury showing the epithelial gap (EG), wound width (WW), and regenerating dermal tissue (RDT).
(D–F) Sections similar to that in (C) were analyzed for the epithelial gap (D), wound width (E), and new dermal tissue (F). Student’s t test; *p < 0.05 for the comparison between Sox2fl/fl;Cre+Tam and controls (the three control groups were pooled because they were statistically similar).
(G and H) Sections similar to that in (C) were immunostained for Ki67, and the percentage of positive cells at the leading edge of the regenerating dermis (ovals in G, magnified in the right panel) was quantified (H). Arrows indicate Ki67-positive cells. One-way ANOVA; ***p = 0.0001 relative to control groups; n = 5 C57/Bl6+Oil, 3 C57Bl6+Tam,4 Sox2fl/fl;Cre+Oil, 7 Sox2fl/fl;Cre+Tam.
(I–K) Sections adjacent to those used for proliferation analysis were immunostained for p75NTR (I) and analyzed for the total area (J) and density (K) of p75NTR-positive cells in the wound bed. Arrows in the inset indicate p75NTR-positive cells. Student’s t test; *p < 0.05; n = 4 Sox2fl/fl;Cre+Oil and 7 Sox2fl/fl;Cre+Tam.
Scale bars, 1 mm (C), 500 μm and 125 μm (G, right and left panels, respectively), 85 μm (I), and 45 μm (inset). See also Figure S2.
