Figure 1.
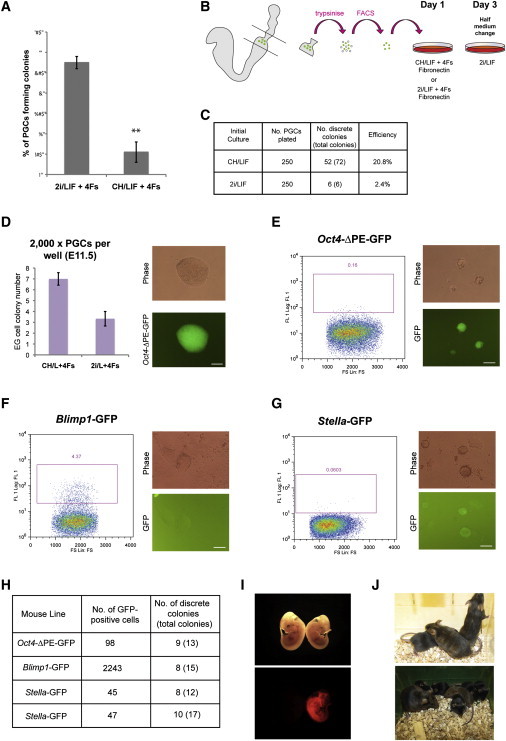
Efficient EG Cell Derivation in Defined Conditions without Serum or Feeders
(A) Histogram showing EG-cell-colony frequency in 2i/LIF versus CH/LIF. The four factors (4Fs), bFGF, SCF, FK, and RA, were added for the first 48 hr of culture. Error bars denote SE of two biological replicates. **p < 0.01, Student’s t test.
(B) Schematic of derivation protocol. PGCs were plated in CH/LIF plus 4Fs, with or without PD for the first 48 hr. All cultures were subsequently fed with 2i/LIF.
(C) Quantitation of EG-cell-colony frequency in each condition.
(D) Histogram showing EG-cell-colony formation from E11.5 PGCs in 2i/LIF and CH/LIF. The four factors (4Fs), bFGF, SCF, FK, and RA, were added for the first 48 hr of culture. All cultures were subsequently fed with 2i/LIF. Error bars denote SE of three biological replicates. Phase and fluorescence images show a primary E11.5 EG cell colony.
(E–G) FACS plot showing gated GFP-positive E8.5 PGCs and phase-contrast and fluorescence images of primary EG cell colonies derived from (E) Oct4-ΔPE-GFP embryos, (F) Blimp1-GFP embryos, and (G) Stella-GFP embryos.
(H) Summary of E7.5 EG-cell-derivation experiments.
(I) Bright-field and fluorescence images of E11.5 chimeric embryos made from aggregations of E7.5 EG cells carrying a constitutively active DsRed reporter transgene.
(J) Coat color chimeras generated with agouti E7.5 EG cells injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts (upper panel) and an adult chimera with C57BL/6 mate and brown pup, indicating transmission of the EG cell genome (lower panel).
