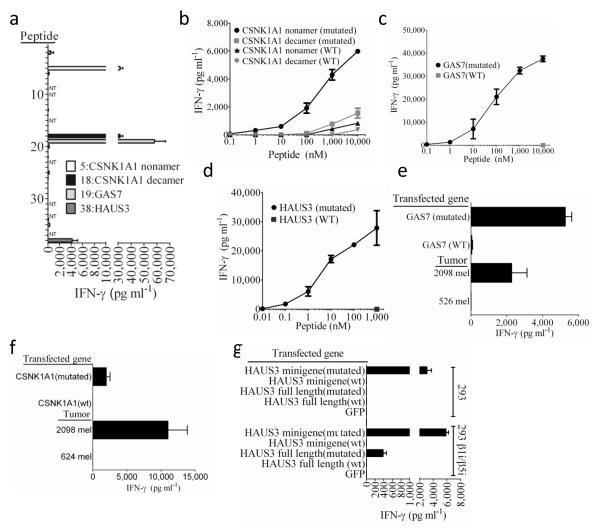
Figure 1. Response of TIL 2098 to candidate epitopes identified from autologous tumors.
(a) A screening assay was carried out to evaluate the release of IFN-γ from TIL 2098 in an overnight co-culture with peptide-pulsed T2 cells that were pulsed individually with the top 61 candidate HLA-A*0201 binding peptides (Supplementary Table 1) identified from 2098 mel, with the exception of peptides 9,10,14,23,24,31,33 and 37, which overlapped with peptides 1,4,4,25,12,15,16 and 4, respectively (NT). Peptides 39-62 (Supplementary Table 1) stimulated the release of 100 pg/ml or less of IFN-γ from TIL 2098 and are not depicted in this graph. The autologous 2098 mel stimulate the release of 10,000 pg/ml of IFN-γ from 2098 TIL in this assay. (b-d) T2 cells were pulsed with tittered doses of the indicated mutated or wild type (WT) peptides, and IFN-γ release measured in an overnight co-culture with TIL 2098. (e) Stable transfected of COS7 cells (COS-A2) expressing HLA-A*0201 were transiently transfected with the indicated transcripts and evaluated for their ability to stimulate IFN-γ release from TIL 2098 in an overnight co-culture. (f) 293 cells were transiently transfected with a construct encoding HLA-*0201 as well as the indicated transcripts and evaluated for their ability to stimulate IFN-γ release from TIL 2098 in an overnight co-culture.