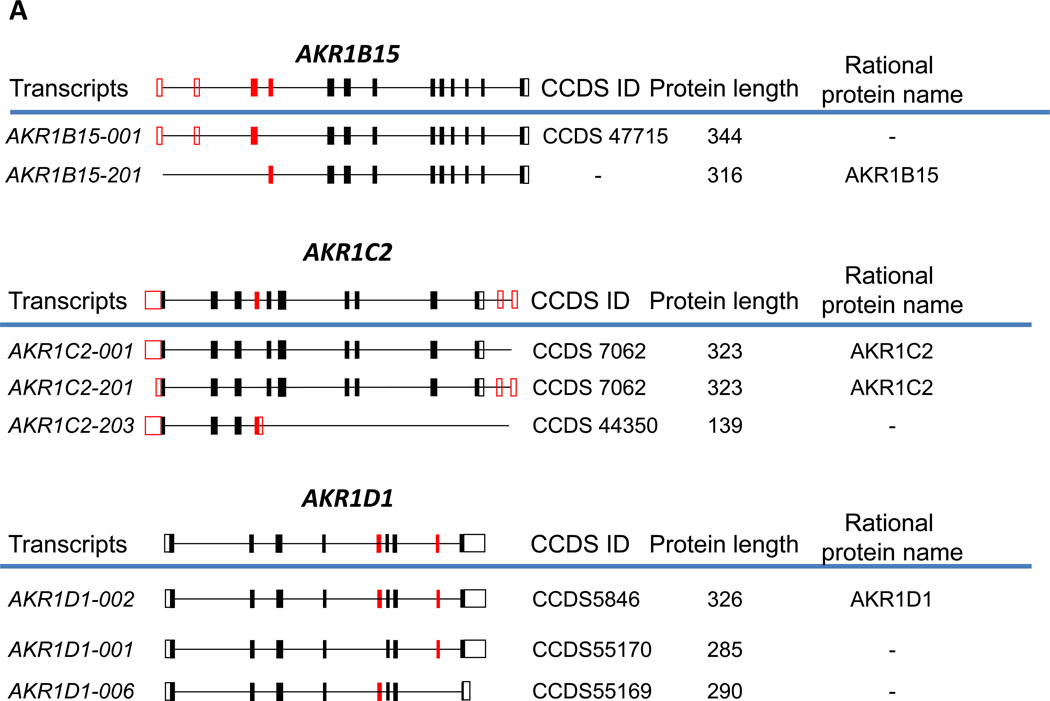
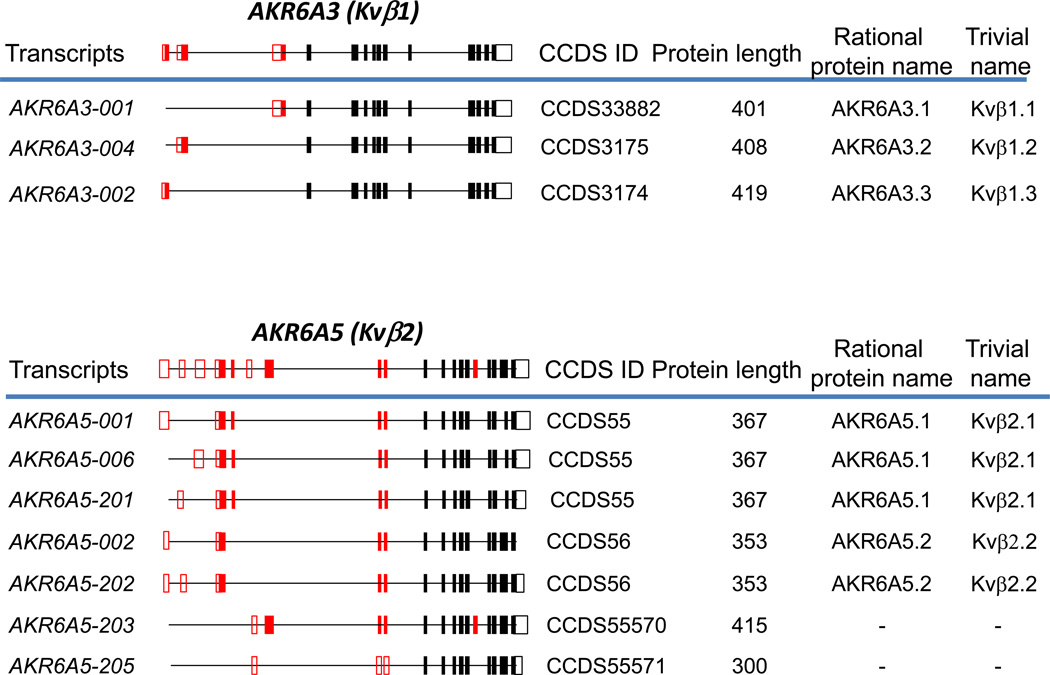
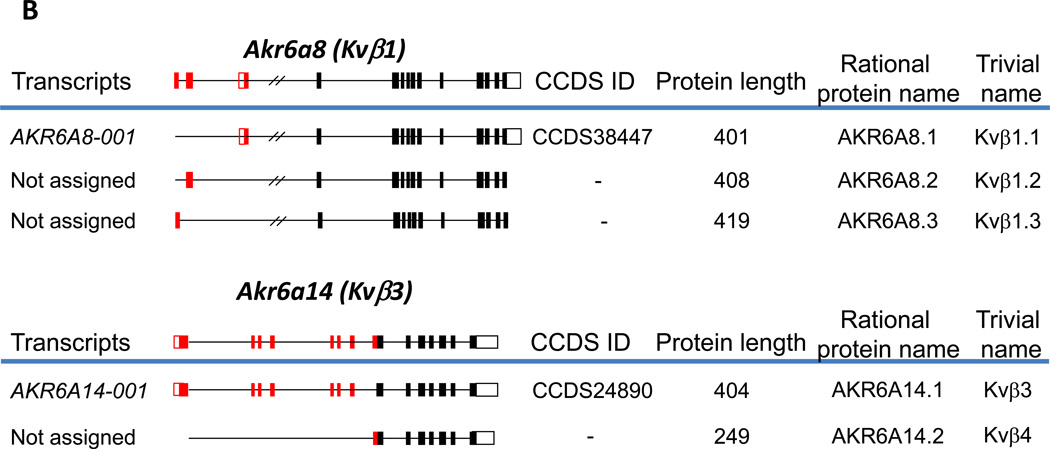
Fig. 1. Alternative splicing of human (A) and murine (B) AKR genes.
Genes with multiple CCDS IDs assigned to them, or genes for which multiple protein isoforms have been reported in the peer-reviewed literature are shown. Constitutive exons are shown in black, and alternatively spliced exons are in red. Solid boxes indicate coding regions, and open boxes indicate untranslated regions. The complete gene structures are shown above the blue lines; below the blue lines are processed transcripts showing only exons included in a particular transcript, along with systematic transcript name, CCDS ID, and the length of the encoded protein. The rational name of the protein isoform encoded by the corresponding alternatively spliced transcript according to the new nomenclature is shown to the right of that transcript. The structure of murine Akr6a8 is drawn according to [15], and that of Akr6a14 is from [20].