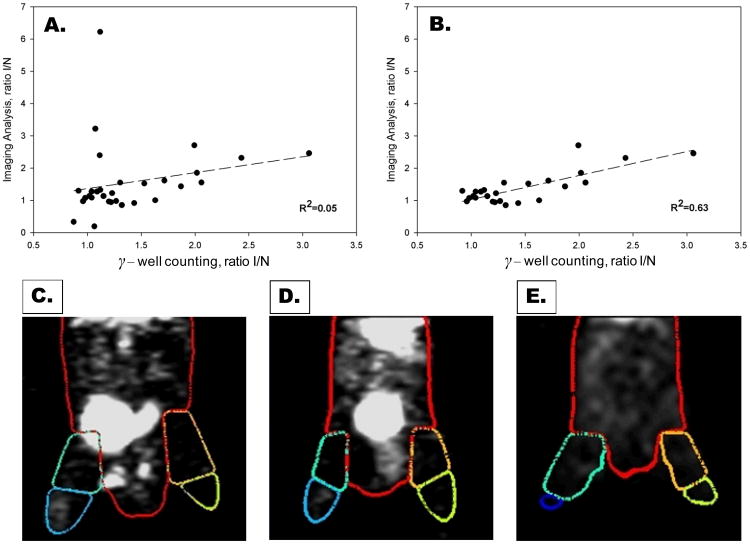
Figure 2. Validation of microSPECT-CT image analysis approach.
Correlation between ischemic-to-nonischemic (I/NI) ratios of counts calculated from image analysis and gamma well counting for both proximal and distal regions (A). The correlation was poor (R2=0.05) when all proximal and distal regions were included (A). The correlation coefficient between imaging analysis and gamma well counting improved significantly (R2=0.63) after proximal regions contaminated with scatter from radioactivity in the bladder have been removed from the analysis (B). Shown below are representative 99mTc-NC100692 microSPECT-CT images from three mice at 7 days after surgical ligation of right femoral artery with superimposed VOIs. Figure 2 C illustrates a mouse with radioactivity within bladder which falls within the right proximal VOI, resulting in overestimation of counts in ischemic (right) relative to non-ischemic (left) proximal leg. Figure 2 D illustrates a second mouse with bladder located centrally in the body and no significant contamination of proximal hindlimb VOIs. Figure 2E illustrates images from third mouse following removal of the radioactive urine from the bladder by needle aspiration immediately before SPECT acquisition.